I. Introduction
Explanation of gas CFDs
Gas CFDs (contracts for difference) allow traders to speculate on the price movements of natural gas without owning the underlying asset. In a CFD, traders initiate an agreement with a broker to exchange the difference in natural gas prices between the opening and closing of the contract.
The importance of understanding the factors that influence gas prices in CFD trading
Understanding the factors that influence gas prices is paramount for effective CFD trading. Natural gas prices are affected by numerous factors, such as supply and demand dynamics, weather patterns, geopolitical events, and government policies. Ignorance of these factors can result in significant losses, especially since gas prices can be highly volatile.
To begin with, supply and demand dynamics play a crucial role in determining gas prices. For instance, if natural gas supply is low and demand is high, the gas price will increase, and vice versa.
II. Supply and Demand
Explanation of supply and demand theory in gas trading
Supply and demand theory is a fundamental economic principle that significantly determines gas prices in trading. According to this theory, the price of a commodity is determined by the intersection of the supply and demand curves. When the supply of a commodity is high and the demand is low, the commodity's price tends to be low. Conversely, when the supply is low, and the demand is high, the price tends to be high.
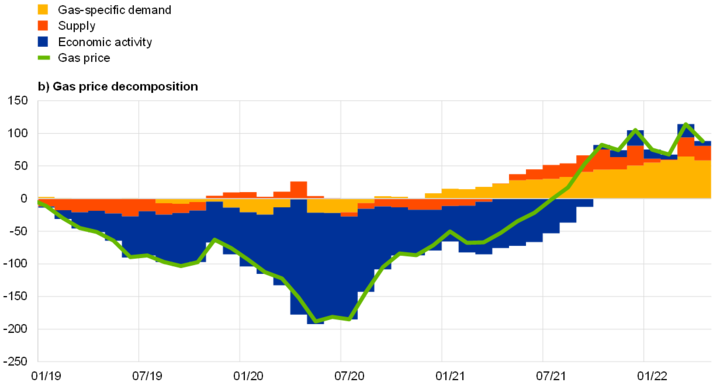
Gas price dynamics (EU)
In the gas trading market, this theory applies as well. When the natural gas supply is high and the demand is low, gas prices tend to be low, and vice versa. For instance, during periods of low demand, such as the summer months, gas prices tend to be low since there is abundant supply. Conversely, during the winter months, gas prices tend to be high due to the high demand for heating.
The effect of high and low supply on gas prices
The effect of high and low supply on gas prices is significant and can significantly impact the natural gas market. When the natural gas supply is high, gas prices tend to decrease due to the surplus of gas available for consumption. Conversely, when the supply is low, gas prices tend to increase due to the gas shortage available for consumption.
When the natural gas supply is high, it is often due to various factors, such as increased production, improved transportation infrastructure, or reduced consumer demand. For example, natural gas demand may be lower during mild weather conditions, leading to increased supply and lower prices. In this scenario, natural gas producers may reduce production or store surplus gas until prices increase.
On the other hand, when the natural gas supply is low, it is often due to reduced production, increased demand, or infrastructure disruptions. For example, during periods of high demand, such as the cold winter months, natural gas supply may be lower due to increased consumption. This can lead to higher gas prices as producers work to meet demand and storage levels decrease.
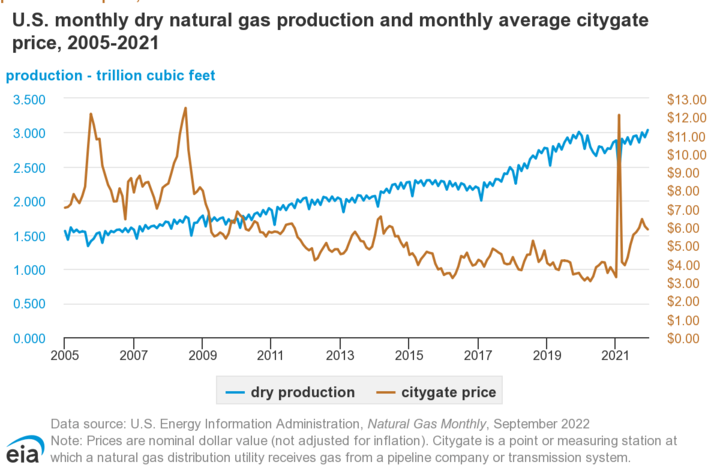
The effect of high and low demand on gas prices
The effect of high and low demand on gas prices is significant and can significantly impact the natural gas market. When the demand for natural gas is high, gas prices tend to increase due to higher gas consumption. Conversely, when demand is low, gas prices tend to decrease due to lower consumption.
For example, during the cold winter, the demand for natural gas for heating increases, resulting in higher gas prices. Similarly, during periods of high economic growth or increased industrial activity, demand for natural gas may increase due to increased production, leading to higher gas prices.
In contrast, when the demand for natural gas is low, gas prices tend to decrease due to reduced consumption. For example, during mild weather conditions, the demand for natural gas may decrease, leading to a surplus of gas and lower prices.

III. Energy Prices
Explanation of the relationship between gas and other energy sources, such as oil and coal
The relationship between gas and other energy sources, such as oil and coal, is complex and can be influenced by various factors. Natural gas, oil, and coal are all fossil fuels used as primary energy sources worldwide. While each energy source has unique properties and applications, there are several ways in which they are related.
Firstly, natural gas and oil are often found together in underground reservoirs. This means that gas and oil production can be interconnected, with the production of one fuel affecting the production of the other. In addition, gas can be used as a substitute for oil in many applications, such as transportation and electricity generation. When oil prices increase, gas can become a more attractive alternative, leading to increased demand for gas and higher gas prices.
The impact of energy price trends on gas CFD trading
Energy price trends have a significant effect on gas CFD trading. This is because natural gas prices are closely related to other energy commodities, such as oil and coal, and are influenced by similar factors, such as global supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical tensions, and weather patterns.
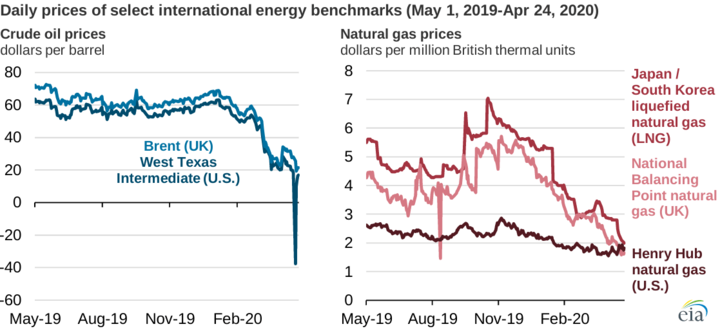
When energy prices trend upward, natural gas prices follow suit. High energy prices can increase demand for natural gas as an alternative energy source. Additionally, high energy prices can make natural gas production more profitable, increasing supply and higher prices.
Conversely, natural gas prices may decrease when energy prices trend downward. This can occur due to lower demand for natural gas as consumers switch to cheaper alternatives or due to lower production costs for natural gas producers.
IV. Weather Patterns
The correlation between weather patterns and gas demand
Weather patterns significantly impact gas demand, making it an essential factor for traders to consider when trading gas CFDs. Natural gas is used for various purposes, including heating homes and buildings, generating electricity, and powering industrial processes. As such, gas demand tends to increase during cold weather and decrease during milder weather.
During cold weather, consumers tend to use more natural gas for heating, increasing gas demand. This can lead to higher gas prices as demand outstrips supply. Conversely, gas demand may decrease during mild weather, lowering gas prices.
The impact of weather patterns on gas demand can vary depending on the region. For example, in areas with a temperate climate, such as the United Kingdom, gas demand tends to increase during the winter months when temperatures drop. In contrast, in hotter regions like the Middle East, gas demand may increase during summer when temperatures rise and air conditioning use increases.
The effects of cold and warm weather on gas prices
Cold and warm weather can significantly impact gas prices in the market. During colder weather, gas demand increases as households and businesses require more natural gas for heating. This increase in demand leads to a higher price for gas. Conversely, gas demand may decrease during warmer weather, lowering gas prices.
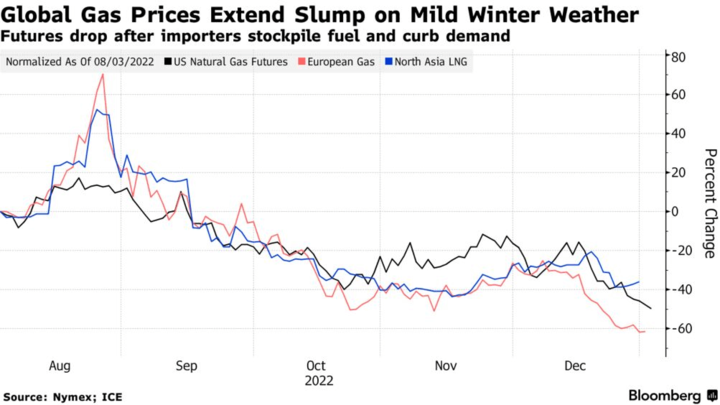
The impact of cold weather on gas prices can be particularly pronounced in regions that experience harsh winters. For example, in the United States, gas prices tend to increase during the winter months as demand for heating rises. This increase in demand can also be influenced by weather-related events such as snowstorms or cold snaps.
In contrast, warm weather tends to decrease gas prices as demand for heating decreases. This effect is more pronounced in regions that experience hot summers, such as the Middle East. During these periods, air conditioning use increases, leading to a rise in gas demand and prices.
V. Gas Storage Levels
The significance of gas storage levels in gas trading
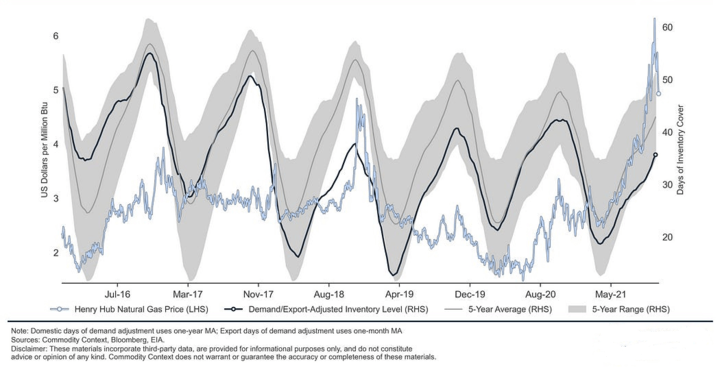
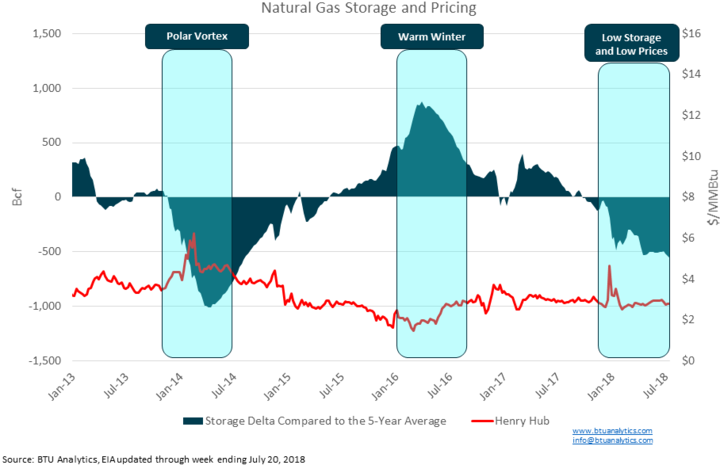
Gas storage levels are critical in gas trading because they significantly impact gas prices. Natural gas storage facilities are used to store excess gas during periods of low demand and release it during periods of high demand. When storage levels are low, it can indicate a tight gas supply, leading to higher prices. Conversely, high storage levels can signal an oversupply of gas, leading to lower prices.
The impact of low and high storage levels on gas prices
Low and high storage levels can significantly impact gas prices in the market. When storage levels are low, it can indicate a tight gas supply, leading to higher prices. This is because when demand increases, there may not be enough gas in storage to meet the demand, leading to competition for limited supply and higher prices.
Conversely, when storage levels are high, it can indicate an oversupply of gas, leading to lower prices. This is because when supply exceeds demand, excess gas may need to be sold, leading to competition among sellers and lower prices.
VI. Economic Indicators
The relevance of economic indicators in gas trading
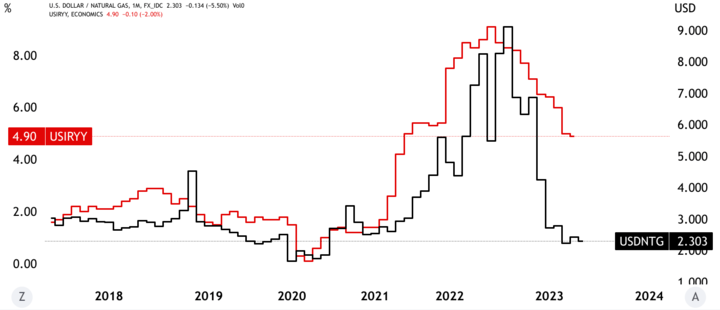
Economic indicators are essential in gas trading because they provide insights into the overall economy's health and potential impact on gas prices. Economic indicators include measures such as gross domestic product (GDP), inflation rates, employment data, consumer spending, and interest rates.
For example, if GDP is growing, it can indicate that demand for gas may increase as industries expand and require more energy. Similarly, if consumer spending is rising, it can indicate that demand for gas from households may also increase. Inflation and interest rates can also impact gas prices, as higher rates can lead to increased costs for producers and potentially higher prices for consumers.
The relationship between indicators such as GDP, employment rates, and gas prices
There is a relationship between economic indicators such as GDP, employment rates, and gas prices. GDP quantifies a country's economic output and is closely correlated with energy demand. As the GDP grows, so does the demand for energy, including natural gas. In this way, GDP growth can lead to higher gas prices as demand increases.
Employment rates can also have an impact on gas prices. When employment rates are high, it can indicate a growing economy with increased energy demand. This can lead to higher gas prices. Conversely, if employment rates are low, it can indicate a weaker economy with lower energy demand, which can lead to lower gas prices.
Inflation rates and interest rates can also have an impact on gas prices. Higher inflation and interest rates can increase costs for producers, potentially leading to higher prices for consumers. Conversely, lower inflation and interest rates can lead to lower costs for producers and potentially lower consumer prices.
VII. Political Events
The effect of policy decisions on gas prices
Policy decisions can have a significant impact on gas prices. For example, government policies that promote natural gas utility as a cleaner alternative to oil and coal can increase demand for natural gas and lead to higher prices. Conversely, policies that discourage the use of natural gas or promote alternative energy sources can decrease demand for natural gas and lead to lower prices.
In addition to government policies, decisions made by major gas-producing and exporting countries can also impact gas prices. For example, OPEC and its member countries significantly influence global oil prices through their production and export decisions.
The impact of tensions between countries and regulations on the gas industry
Tensions between countries and regulations can significantly impact the gas industry, affecting gas prices and CFD trading.
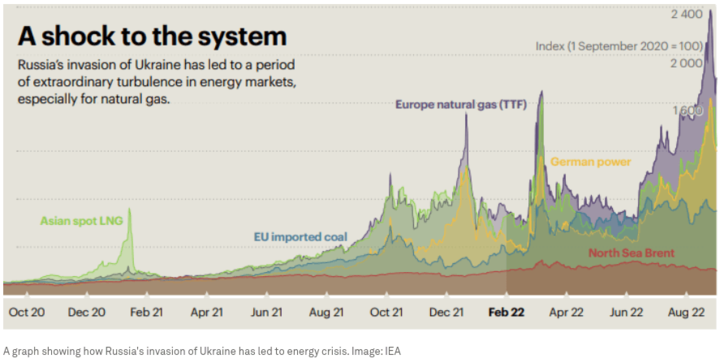
For example, political tensions between gas-producing countries (like Russia) can lead to disruptions in gas supply, which can cause prices to rise due to reduced availability. Similarly, regulation changes that affect gas production, transportation, or distribution can also impact gas prices. For instance, stricter environmental regulations may increase gas production and transportation costs, leading to higher prices.
Regulations can also impact the demand for gas. For example, policies that promote the use of renewable energy or energy efficiency measures can reduce the demand for natural gas and lead to lower prices.
In addition, trade policies can impact the gas industry. For instance, tariffs and other trade barriers can affect gas flow across borders and prices.
VIII. Exploration and Production Trends
The relationship between exploration and production trends and gas prices
The relationship can be complex, involving supply and demand dynamics and geopolitical and economic factors. Exploration trends refer to the natural gas reserves being discovered and developed, while production trends refer to the amount of natural gas being extracted and made available for consumption.
If exploration trends are solid and significant new reserves are discovered, it can increase supply and potentially lower prices. However, if exploration trends are weak and further reserves are not found, it can lead to decreased supply and potentially higher prices.
Similarly, if production trends are strong and more natural gas is extracted and made available for consumption, it can increase supply and potentially lower prices. Conversely, if production trends are weak and natural gas extraction is declining, it can lead to decreased supply and potentially higher prices.
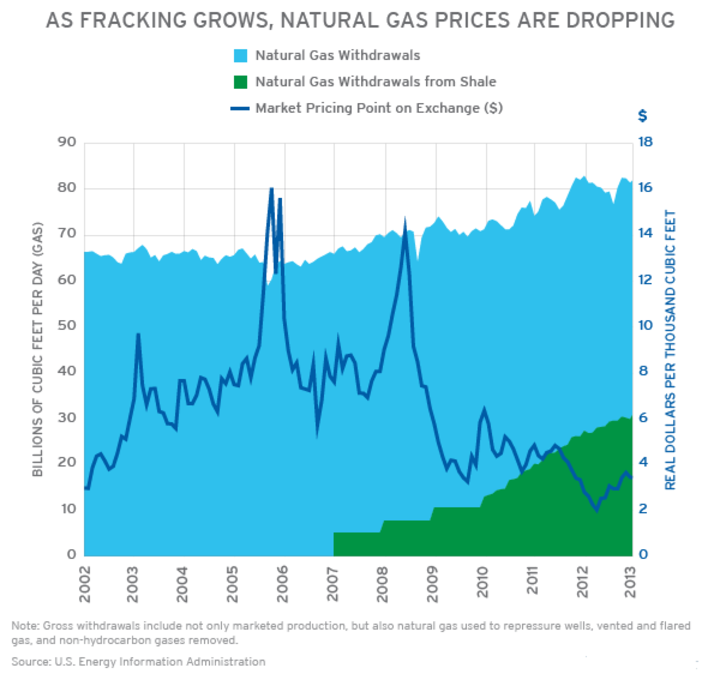
The effect of changes in exploration and production techniques on gas prices
Changes in exploration and production techniques can significantly impact gas prices. Exploration techniques refer to the methods used to locate and identify natural gas reserves, while production techniques refer to the methods used to extract natural gas from the ground.
Advancements in exploration techniques, such as 3D seismic imaging and directional drilling, have allowed for more efficient and effective exploration of natural gas reserves. It has led to an enhancement in the natural gas reserves discovered, which can result in increased supply and potentially lower prices.
Similarly, advancements in production techniques, such as hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling, have allowed for more efficient extraction of natural gas from shale formations. It has enhanced natural gas production, increasing supply and potentially lowering prices.
However, changes in exploration and production techniques can also negatively impact the environment, leading to increased regulations and costs to producers. This can lead to decreased production and potentially higher prices.
IX. LNG Developments
The effects of LNG exports and imports on gas prices
The impacts of liquefied natural gas (LNG) exports and imports on gas prices can be complex and depend on various factors.
LNG exports involve the transport of natural gas in liquid form to other countries. This can have several effects on gas prices in the exporting country. First, increased exports can reduce domestic supply, leading to higher prices. Second, exports can increase demand for natural gas, leading to higher prices. Finally, the increased global demand for natural gas due to exports can lead to higher prices overall.
On the other hand, LNG imports can increase domestic supply and potentially lower gas prices in the importing country. Imports can also provide a gas source during high demand or supply shortages.
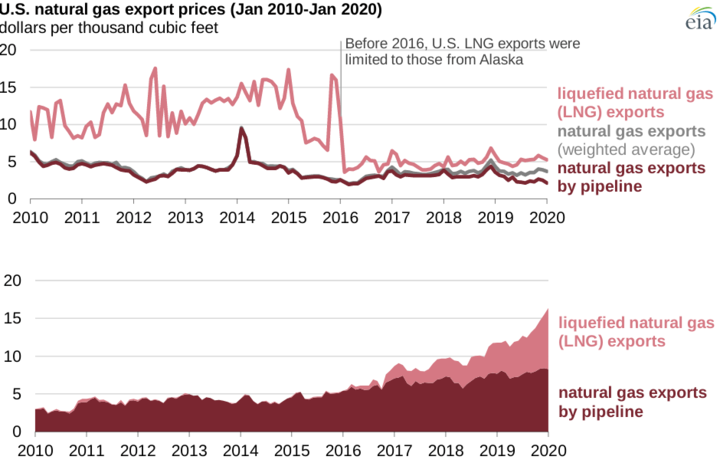
The impact of LNG developments on gas trading
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) developments have significantly impacted domestic and international gas trading.
The global LNG market has proliferated in recent years, with an increasing number of countries importing and exporting LNG. This has led to more liquid and interconnected markets, making it easier for traders to buy and sell gas across borders. Additionally, the growth of LNG has increased the availability of gas in previously underserved markets, such as Asia and Europe, which has helped to balance supply and demand and reduce price volatility.
LNG developments have also had an impact on gas production and infrastructure. For example, many countries have invested in building LNG export terminals, which can help monetize stranded gas reserves and increase production. This can lower domestic gas prices in the short term as excess gas is exported to international markets. However, over the longer term, increased exports can increase domestic gas prices as supply becomes tighter.
X. Market Sentiment
The importance of market sentiment in gas CFD trading
Market sentiment signifies the overall attitude of investors and traders towards a particular market or asset, which is vital in gas CFD trading. Understanding market sentiment is important because it can help traders anticipate potential price movements and make informed trading decisions.
The effect of bullish and bearish sentiment on gas prices
Bullish and bearish sentiment can significantly impact gas prices in CFD trading. Bullish sentiment is when investors and traders are optimistic about the future performance of an asset, while bearish sentiment is when they are pessimistic.

In the case of gas CFD trading, bullish sentiment can lead to increased demand for gas contracts, which can drive up prices. This could happen if higher gas demand is expected due to cold weather or increased economic activity. On the other hand, bearish sentiment can lead to decreased demand for gas contracts and lower prices. This could occur if there are expectations of lower gas demand due to warmer weather or decreased economic activity.
XI. Speculation
The influence of speculation on gas prices
Speculation can have a significant influence on gas prices in CFD trading. Speculators are traders who take positions in gas contracts to profit from price movements. While speculators are often criticized for contributing to price volatility, they can also play an essential role in providing liquidity and market efficiency.
When there is a high level of speculation in the gas market, it can lead to increased price volatility. This is because speculators may make trades based on their expectations of future gas prices rather than the market's underlying supply and demand fundamentals. As a result, price movements may be driven more by speculation than actual gas supply and demand changes.

The significance of trader sentiment and market trends in identifying trading opportunities
Trader sentiment and market trends can be significant factors in identifying potential trading opportunities in gas CFD trading. By monitoring trader sentiment, traders can gain insights into how the market is likely to behave and where potential opportunities may arise. For example, if traders are generally bullish on gas, it may indicate that prices are likely to rise, which could present a buying opportunity. On the other hand, if traders are bearish on gas, it may suggest that prices are likely to fall, creating a potential selling opportunity.
Similarly, market trends can also provide valuable insights into trading opportunities. By analyzing historical price data and identifying patterns and trends, traders can better understand how the market behaves and where potential opportunities may arise. For example, if there is a consistent upward trend in gas prices over time, it may suggest that prices are likely to continue rising, presenting a buying opportunity.
XII. Strategies for Profiting from Gas CFDs
Trading strategies for gas CFDs based on the factors discussed in the previous sections


● Supply and Demand: Monitor gas production levels, pipeline capacity, and consumption trends. Look for imbalances in supply and demand that can affect prices. If demand is outpacing supply, consider buying gas CFDs; if supply is outstripping demand, consider selling them.
● Energy Prices: Keep a close eye on crude oil and other energy prices, as gas prices tend to move in tandem. Watch for changes in global supply and demand dynamics that may affect energy prices and gas CFDs.
● Weather Patterns: Weather can significantly impact gas demand, especially during extreme hot or cold temperatures. Keep track of weather forecasts and adjust your trading positions accordingly.
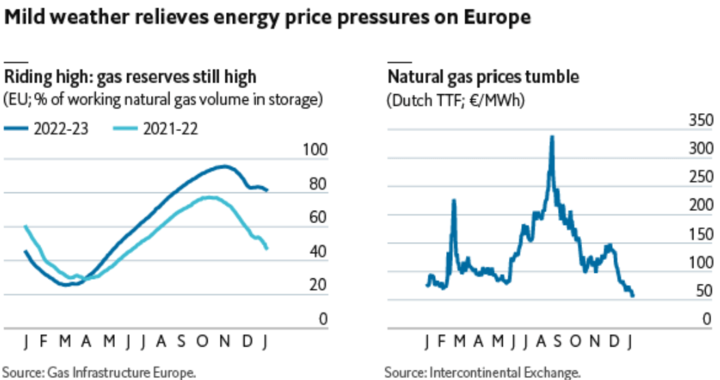
● Gas Storage Levels: Track gas storage levels, as they can influence gas prices. Low storage levels may indicate increased demand, which can increase prices, while high storage levels may lead to lower prices.
● Economic Indicators: Monitor economic indicators such as GDP, employment figures, and inflation rates. Positive economic news may indicate increased demand for gas, which can drive prices higher.
● Political Events: Stay informed about geopolitical events affecting gas prices and adjust your trading positions accordingly.
● Exploration and Production Trends: Follow trends in gas exploration and production, including technological advancements, new discoveries, and changes in regulatory frameworks. These factors can influence supply levels and, ultimately, prices.
● LNG Developments: Monitor developments in the LNG market, including new facilities and trade agreements. LNG exports can have a significant impact on global gas prices and CFDs.
● Market Sentiment: Watch market sentiment and investor sentiment towards gas and energy. Positive sentiment can lead to increased demand for gas, while negative sentiment can lead to lower prices.
● Speculation: Monitor speculation and market rumors that may affect gas prices. Take advantage of market volatility to make profitable trades.
Examples of successful trading strategies using gas CFDs
● Supply and Demand: For instance, if a cold winter is predicted, there might be an increase in demand for gas for heating, causing prices to rise. Similarly, if a new gas pipeline is built, it can increase supply, leading to lower prices.
● Energy Prices: If crude oil prices rise, it can increase the cost of production for gas, leading to higher gas prices. Conversely, if renewable energy sources become more affordable, it can decrease demand for gas and lower prices.
● Weather Patterns: If there is an unusually hot summer, demand for gas for electricity generation (for air conditioning) may increase, driving up prices. Conversely, if there is a mild winter, demand for gas for heating may decrease, leading to lower prices.
● Gas Storage Levels: For example, if there is a mild winter and gas storage levels are high, it may lead to oversupply and lower prices. Conversely, harsh winters and low storage levels can lead to a gas shortage and higher prices.
● Economic Indicators: If the economy is growing and consumers have more disposable income, there may be an increase in gas consumption for transportation, leading to higher prices. On the other hand, if there is a recession, demand for gas may decrease, leading to lower prices.
● Political Events: For example, if there are tensions between gas-producing countries, it can lead to supply disruptions and higher prices. Additionally, if a new government imposes stricter regulations on the energy sector, it can lead to increased costs and higher gas prices.
● Exploration and Production Trends: If there is a new discovery of natural gas reserves, it can increase supply and lower prices. Similarly, if there is a decline in production due to aging infrastructure or environmental concerns, it can decrease supply and raise prices.
● LNG Developments: For example, if there is an increase in LNG exports from the United States to Europe, it can increase global demand and raise prices. Conversely, if a new LNG plant opens in a gas-producing country, it can increase supply and lower prices.
● Market Sentiment: If traders are optimistic about the economy, it can increase demand for energy, including gas, and drive up prices. Conversely, if there is negative sentiment about the economy or the energy sector, it can lead to lower prices.
● Speculation: For instance, if there is a rumor that there will be a supply disruption in a major gas-producing country, it can cause prices to rise. Similarly, if there is speculation that new technology will reduce demand for gas, it can lead to lower prices.
XIII. Conclusion
A recap of the main points
Gas CFDs allow traders to speculate on the future price movements of natural gas. To trade gas CFDs efficiently, traders need to understand the various factors influencing gas prices. These factors include supply and demand, energy prices, weather patterns, gas storage levels, economic indicators, political events, exploration and production trends, LNG developments, market sentiment, and speculation. Effective gas CFD trading requires careful analysis of market data and a solid understanding of the factors that influence gas prices.
Final thoughts on trading gas CFDs and the role of understanding these factors in successful trading
Understanding the various factors influencing gas prices is crucial for effectively trading gas CFDs. Traders with a comprehensive understanding of these factors can make informed trading decisions, develop effective trading strategies, and manage risk effectively. By staying up-to-date with market trends and news, traders can identify potential opportunities and modify their trading strategies accordingly. Overall, a solid understanding of the factors influencing gas prices is essential for the efficient trading of gas CFDs.