I. Introduction
Definition of Gold CFD
A gold CFD, or contract for difference, is a financial derivative instrument that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of gold without owning the physical asset. In a gold CFD, the buyer and the seller agree to exchange the difference in the price of gold between the opening and closing of the contract. If the price of gold goes up, the buyer makes a profit, and if the price goes down, the seller makes a profit.
Gold CFDs have become increasingly popular in recent years because they offer traders a more accessible and flexible way to invest in gold compared to traditional methods such as purchasing physical gold or investing in gold mining stocks.
The Importance of Understanding Factors That Affect Gold CFD Prices
Understanding the factors that affect gold CFD prices is essential for traders who want to make informed investment decisions. Gold CFD prices are influenced by a range of economic, political, and social factors, and traders must be able to analyze and interpret these factors to accurately predict future price movements and social factors, and traders must be able to analyze and interpret these factors to accurately predict future price movements. In this way, they can make informed investment decisions and manage their risk effectively.
Overview of the factors
The price of gold CFDs is influenced by various factors, including geopolitical, economic, market, and external factors.
Geopolitical factors such as political instability, global tensions, government policies, economic sanctions, wars, and conflicts can affect gold prices. For example, during the Arab Spring in 2011, political instability in the Middle East led to a surge in gold prices.
Economic factors such as interest rates, inflation, currency exchange rates, and supply and demand also impact gold prices. Gold is often seen as a hedge against inflation, and any fluctuations in interest rates can influence the opportunity cost of holding gold. Market factors such as speculation, investor sentiment, stock market movement, and commodity market movement can also impact gold prices. Lastly, external factors such as natural disasters, pandemics, accidents, and unforeseeable events can also affect gold prices.
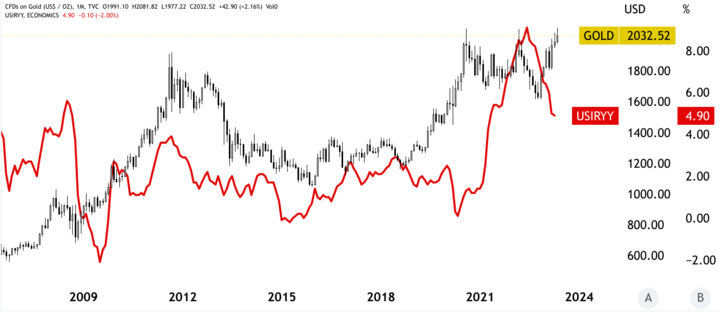
Political instability, for instance, can lead to market uncertainty and volatility, making it essential for traders to monitor political developments closely. Similarly, changes in interest rates can significantly impact the demand for gold, and traders must keep an eye on central bank announcements and policy decisions. Inflation can also influence gold prices, making it crucial for traders to monitor inflation data and other economic indicators.
Market factors such as speculation and investor sentiment can also have a significant impact on gold prices. For example, if investors are optimistic about the economy, they may choose to invest in other assets, leading to a decrease in gold prices. On the other hand, during times of stock market decline, investors may turn to gold as a safe-haven asset, leading to an increase in prices. External factors such as pandemics and natural disasters can also disrupt the gold market, and traders must be prepared to adjust their strategies accordingly.
II. Factors that Affect the Price of Gold CFD
A. Geopolitical Factors
Political Instability
Political instability is a significant geopolitical factor that can impact the price of gold CFDs. When there is political uncertainty in a country or region, investors often shift their assets to safer investments, such as gold. This is because political instability can cause market uncertainty and volatility, leading investors to seek assets that are not affected by political events.

For example, the political instability in Venezuela has led to a surge in demand for gold as a safe-haven asset. The country's economy has been in turmoil with hyperinflation, food and medicine shortages, and political instability. Investors are concerned about the country's economic and political future, and many have turned to gold as a hedge against uncertainty.
Moreover, the ongoing political instability in the United States, including the recent protests and riots, has also affected the price of gold CFDs. Investors are concerned about the impact of the political turmoil on the economy and the potential for market uncertainty, leading to an increase in demand for gold as a safe-haven asset.
Global Tensions
Global tensions are another geopolitical factor that can significantly impact the price of gold CFDs. Any political or economic tension between countries or regions can cause investors to shift their assets to safer investments, such as gold. This is because global tensions can lead to market uncertainty and volatility, making investors seek assets that are not affected by political events.
For example, the ongoing trade war between the United States and China has led to market uncertainty and volatility, driving up demand for gold as a safe-haven asset. The two countries have imposed tariffs on each other's goods, leading to concerns about the impact of the trade war on the global economy. Investors are concerned that the trade war could lead to a recession, which has led to an increase in demand for gold as a hedge against market uncertainty.
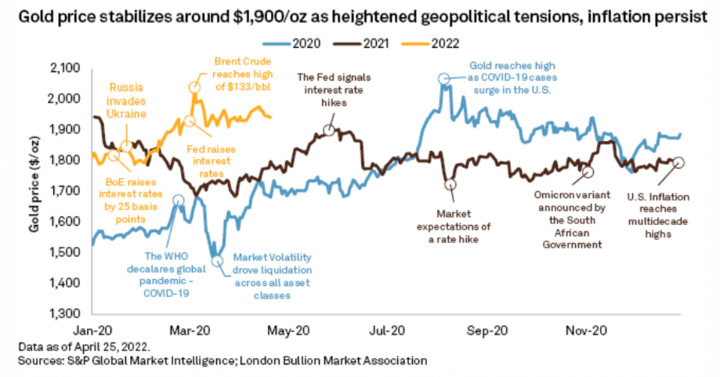
Similarly, tensions between North Korea and the United States have historically led to a surge in demand for gold as a safe-haven asset. The two countries have been engaged in a tense diplomatic standoff over North Korea's nuclear program, causing market uncertainty and volatility. Investors are concerned about the potential impact of a military conflict on the global economy, leading to an increase in demand for gold as a hedge against uncertainty.
Moreover, tensions in the Middle East have historically led to an increase in demand for gold as a safe-haven asset. For instance, the recent tensions between the United States and Iran have led to market uncertainty and volatility, driving up demand for gold as a hedge against uncertainty.
Government Policies
Government policies are a significant geopolitical factor that can impact the price of gold CFDs. Government policies can include changes in regulations, taxation, and monetary policies, among others. These policies can affect the economy and the financial markets, leading to changes in demand for gold.
For example, changes in monetary policy by central banks can significantly impact the price of gold CFDs. When central banks lower interest rates, it reduces the opportunity cost of holding gold, making it more attractive to investors. Conversely, when central banks raise interest rates, it increases the opportunity cost of holding gold, reducing demand for the precious metal.
Moreover, changes in government regulations and taxation policies can also impact the price of gold CFDs. For instance, restrictions on gold imports or exports by governments can limit the supply of gold in the market, leading to an increase in its price. Similarly, changes in taxation policies, such as higher taxes on gold transactions, can reduce demand for the precious metal, leading to a decline in its price.
In addition, political changes such as the election of a new government can also impact the price of gold CFDs. When a new government comes into power, they may implement policies that can significantly impact the economy and the financial markets, leading to changes in demand for gold. For instance, the election of Donald Trump as the U.S. president in 2016 led to a surge in demand for gold as investors sought to hedge against potential market uncertainty caused by his policies.
Economic Sanctions
Economic sanctions are a geopolitical factor that can significantly impact the price of gold CFDs. Economic sanctions are imposed by countries or international organizations against a target country or entity to restrict trade and financial transactions. These sanctions can lead to market uncertainty and volatility, driving up demand for safe-haven assets like gold.
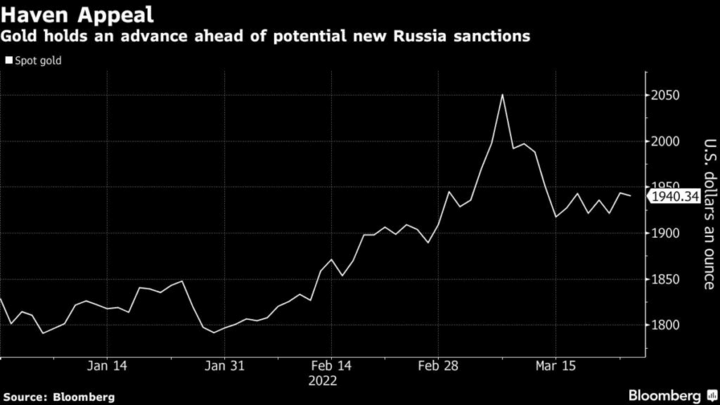
For example, the economic sanctions imposed by the United States and European Union against Russia in 2022 led to a surge in demand for gold as a safe-haven asset. The sanctions were imposed in response to Russia's annexation of Crimea and involvement in the conflict in eastern Ukraine, causing market uncertainty and volatility. Investors sought to hedge against the risk of market volatility caused by the sanctions by investing in gold.
Similarly, the economic sanctions imposed by the United States against Iran have historically led to an increase in demand for gold as a safe-haven asset. The sanctions were imposed in response to Iran's nuclear program and human rights abuses, causing market uncertainty and volatility. Investors sought to hedge against the risk of market volatility caused by the sanctions by investing in gold.
Moreover, economic sanctions can also impact the supply and demand dynamics of gold. For instance, if a country under sanctions is a significant gold producer, the sanctions can limit the supply of gold in the market, leading to an increase in its price. Conversely, if a country under sanctions is a significant gold consumer, the sanctions can reduce demand for gold, leading to a decline in its price.
Wars and Conflicts
Wars and conflicts are a significant geopolitical factor that can impact the price of gold CFDs. Wars and conflicts can lead to market uncertainty and volatility, driving up demand for safe-haven assets like gold.
For example, the war in Syria has led to a surge in demand for gold as a safe-haven asset. The conflict has caused significant market uncertainty and volatility, with investors seeking to hedge against the risk of market volatility by investing in gold. Similarly, the 2022 conflict between Russia and Ukraine led to a surge in demand for gold as a safe-haven asset, with investors seeking to hedge against the risk of market volatility caused by the conflict.
Moreover, wars and conflicts can also impact the supply and demand dynamics of gold. For instance, if a country that is a significant gold producer is involved in a conflict, it can limit the supply of gold in the market, leading to an increase in its price. Conversely, if a country that is a significant gold consumer is involved in a conflict, it can reduce demand for gold, leading to a decline in its price.
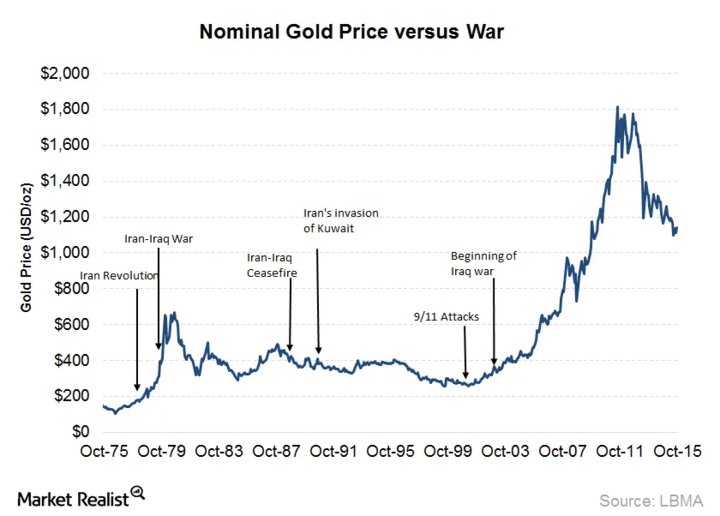
Furthermore, wars and conflicts can also impact the broader economy, leading to changes in monetary policies and regulations that can impact the price of gold. For example, wars and conflicts can lead to changes in interest rates and inflation, which can impact the demand for gold. Similarly, wars and conflicts can lead to changes in government policies, including taxation policies, which can also impact the demand for gold.
B. Economic Factors
Interest Rates
Interest rates are one of the most crucial economic factors that can significantly impact the price of gold CFDs. Interest rates are the rates at which banks borrow or lend money, and changes in interest rates can impact the cost of borrowing and lending, which can impact the demand for gold.
When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes more accessible and less expensive, which can lead to an increase in consumer and business spending. This increased spending can lead to economic growth and inflation, leading to a decline in the value of the currency and an increase in demand for safe-haven assets like gold. Conversely, when interest rates are high, borrowing becomes more expensive, leading to a decline in consumer and business spending, lower economic growth and inflation, and a decrease in demand for safe-haven assets like gold.
For example, in response to the 2008 global financial crisis, central banks worldwide cut interest rates to stimulate economic growth. This led to a surge in demand for gold as a safe-haven asset, with investors seeking to hedge against the risk of market volatility caused by the crisis. Similarly, in 2020, the US Federal Reserve cut interest rates to near zero to support the economy during the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to a surge in demand for gold as a safe-haven asset.
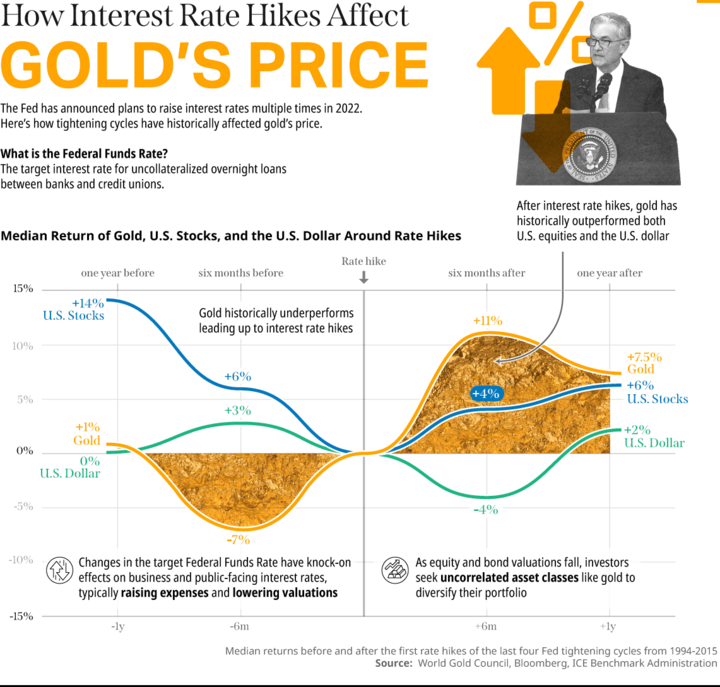
Moreover, changes in interest rates can impact the value of the currency, which can also impact the demand for gold. When interest rates rise, the value of the currency tends to rise as well, making gold more expensive for foreign investors and leading to a decline in demand for gold. Conversely, when interest rates decline, the value of the currency tends to decline, making gold less expensive for foreign investors and leading to an increase in demand for gold.
Inflation
Inflation is another economic factor that can significantly impact the price of gold CFDs. Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and when inflation is high, the value of the currency tends to decline, leading to an increase in demand for safe-haven assets like gold.
When inflation is high, investors and traders may seek to invest in gold as a hedge against inflation, as gold has historically maintained its value during periods of high inflation. Gold is often viewed as a store of value that can protect investors' purchasing power in the face of rising prices.
For example, during the 1970s, the US experienced high levels of inflation due to the oil crisis, leading to a surge in demand for gold as a hedge against inflation. The price of gold rose from around $35 per ounce in 1970 to around $800 per ounce by 1980. Similarly, in 2011, gold prices hit an all-time high of $1,900 per ounce in response to concerns about inflation caused by the US Federal Reserve's quantitative easing program.
Moreover, inflation can impact the value of the currency, which can also impact the demand for gold. When inflation is high, the value of the currency tends to decline, making gold more attractive as a safe-haven asset for investors seeking to protect their investments against the currency's loss of value.
Currency Exchange Rates
Currency exchange rates are another economic factor that can affect the price of gold CFDs. Gold is priced in US dollars globally, so changes in the exchange rate of the US dollar against other currencies can impact the price of gold. If the US dollar strengthens against other currencies, the price of gold tends to fall, and vice versa.
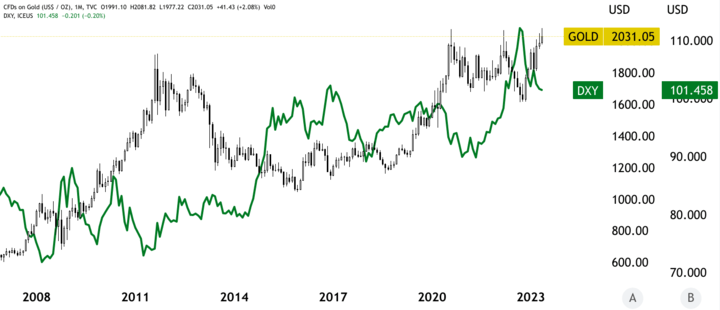
For example, in 2020, the US dollar experienced a significant decline against major currencies, including the euro and the Japanese yen, due to the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. As a result, the price of gold rose to all-time highs as investors sought to invest in gold as a safe-haven asset.
Similarly, in 2018, the US dollar experienced a significant rally against other currencies, leading to a decline in the price of gold. This was due to a combination of factors, including rising US interest rates, a strong US economy, and concerns about trade tensions between the US and China.
Changes in exchange rates can also impact the demand for gold from investors in different countries. For example, if the exchange rate of a currency weakens, investors in that country may find it more expensive to buy gold in US dollars, leading to a decline in demand for gold in that country. Conversely, if the exchange rate of a currency strengthens, investors in that country may find it cheaper to buy gold in US dollars, leading to an increase in demand for gold.
Supply and Demand
Supply and demand are critical economic factors that can affect the price of gold CFDs. The supply of gold is limited, and it cannot be easily increased, so changes in demand can have a significant impact on the price of gold.

Increased demand for gold can result from various factors, such as economic uncertainty, inflation, and geopolitical tensions. For example, if investors are concerned about the state of the economy or expect inflation, they may buy gold as a safe-haven asset to protect their wealth. Similarly, if there is political instability or geopolitical tension, investors may also seek refuge in gold.
On the other hand, if demand for gold decreases, the price of gold may fall. Factors that can lead to a decrease in demand for gold include a strong economy, lower inflation, or alternative investments with higher returns.
Supply factors can also impact the price of gold CFDs. The mining and production of gold can be affected by various factors, such as political instability, labor strikes, and natural disasters. These can lead to disruptions in supply and ultimately impact the price of gold.

For example, in 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic caused significant disruptions to gold mining and production, leading to supply shortages and a rise in the price of gold. Similarly, in 2018, labor strikes in South Africa, one of the world's largest gold producers, led to a reduction in gold supply and an increase in the price of gold.
C. Market Factors
Speculation
Speculation is one of the significant market factors that can influence the price of gold CFDs. Speculators purchase gold with the intent of selling it later for a profit. The behavior of speculators can significantly impact the supply and demand for gold, leading to changes in prices.
Speculators can engage in short-term or long-term trades, depending on their investment strategies. For instance, short-term speculators can buy gold with the hope of profiting from a price increase within a short period, such as a few hours or days. On the other hand, long-term speculators can hold onto gold for a longer period, sometimes even years, with the hope of profiting from a price increase over time.
Speculation can impact the price of gold by creating market volatility, which can result in rapid price movements. For example, if a significant investor or a hedge fund takes a large position in gold, this can lead to a sudden increase in demand, which can drive up the price of gold. Similarly, if the market perceives that the demand for gold will decrease, such as when there is a significant shift in economic or political conditions, the price of gold may fall.
In some cases, speculative behavior can also lead to price bubbles, where the price of gold is driven up to unsustainable levels, and when the bubble bursts, there can be a significant decline in the price of gold. For instance, in the late 1970s and early 1980s, the price of gold experienced a significant bubble, driven by speculation and concerns over inflation. The bubble eventually burst, leading to a substantial drop in the price of gold.
Investor Sentiment
Investor sentiment is another important market factor that can affect the price of gold CFDs. Investor sentiment refers to the overall attitude or mood of market participants towards a particular asset, such as gold. Positive investor sentiment can lead to increased demand for gold, which can drive up the price, while negative sentiment can lead to decreased demand, which can cause the price to fall.
For instance, if investors are optimistic about the global economic outlook, they may invest more in riskier assets such as stocks, which can lead to decreased demand for gold as a safe-haven asset. On the other hand, if investors are worried about economic and political conditions, they may flock to gold as a safe-haven asset, leading to increased demand and driving up the price.
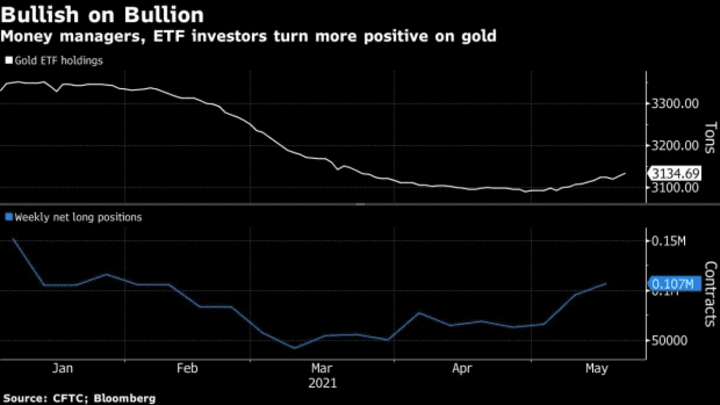
Investor sentiment can also be influenced by various economic indicators and events, such as interest rate announcements, GDP growth, and geopolitical tensions. For example, if there is a sudden increase in geopolitical tensions, investors may become more risk-averse and move their investments towards safe-haven assets such as gold.
Furthermore, investor sentiment can also be influenced by news and media reports. For instance, if there is a sudden increase in inflation, news outlets may report on the potential negative impact on the economy, which can cause investors to become more pessimistic about the economic outlook and increase demand for gold.
Stock Market Movement
The movement of the stock market is another market factor that can impact the price of gold CFDs. The stock market and gold prices have an inverse relationship, meaning that when one goes up, the other tends to go down.
For example, if the stock market is performing well, investors may shift their investments from gold to stocks, causing a decrease in demand for gold and a decrease in its price. Conversely, if the stock market is performing poorly, investors may move their investments from stocks to gold, causing an increase in demand for gold and an increase in its price.
In addition, the stock market can also indirectly impact the price of gold CFDs through its influence on the economy. For instance, if the stock market experiences a significant downturn, it can have a negative impact on the economy, which can lead to increased demand for safe-haven assets such as gold.
Moreover, some investors use gold as a hedge against stock market volatility. When the stock market experiences a high level of volatility, investors may buy gold to offset potential losses from their stock investments. This can increase the demand for gold and push up its price.
Commodity Market Movement
Commodity market movements can also have an impact on the price of gold CFDs. This is because gold is often considered a commodity and is traded on commodity exchanges alongside other commodities such as oil and silver.
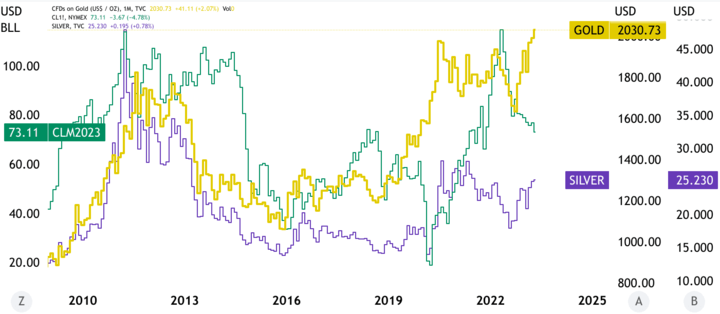
If the prices of other commodities are rising, investors may turn to gold as an alternative investment, leading to an increase in demand for gold and a rise in its price. Conversely, if the prices of other commodities are falling, investors may reduce their holdings in gold, leading to a decrease in demand for gold and a fall in its price.
For example, if the price of oil rises due to increased demand or geopolitical tensions, investors may buy gold as a hedge against potential inflation or economic uncertainty. This can drive up the price of gold CFDs. On the other hand, if the price of oil falls due to oversupply or a decrease in demand, investors may sell their gold holdings to invest in other commodities or assets, leading to a decrease in the price of gold CFDs.
Additionally, commodity market movements can also impact the mining and production of gold. The cost of mining and production can fluctuate based on the prices of other commodities such as energy and labor production can fluctuate based on the prices of other commodities such as energy and labor. If the cost of production rises, it can lead to a decrease in the supply of gold, which can drive up its price.
D. External Factors
Natural Disasters
Natural disasters can have a significant impact on the price of gold CFDs. The occurrence of natural disasters can disrupt the supply chain, which can affect the production and distribution of gold. For example, if a major hurricane or flood hits a region where gold is mined, it can cause significant damage to the mines and delay the production of gold.
In such cases, the supply of gold can decrease, leading to an increase in the price of gold CFDs. This is because the demand for gold remains constant, and with a decrease in supply, the price of gold can go up due to scarcity.
Moreover, natural disasters can also impact the economies of the affected regions, which can have an indirect effect on the price of gold CFDs. For instance, if a natural disaster hits a region with a significant gold industry, it can cause a decline in economic activity and disrupt the markets, leading to a decrease in investor confidence.
Investors may then look for safe-haven assets such as gold to protect their investments from potential losses. This can lead to an increase in demand for gold, driving up its price.
For example, in 2011, a massive earthquake and tsunami hit Japan, causing significant damage to the economy and disrupting supply chains. This led to a decline in economic activity and a fall in the stock market. Investors then turned to gold as a safe-haven asset, which caused an increase in its price.
Pandemics
Pandemics are an example of external factors that can affect the price of gold CFDs. Pandemics are sudden outbreaks of diseases that can spread rapidly across regions and countries, leading to widespread illness and even death. Pandemics can also have significant economic impacts, causing disruptions to supply chains, travel, and trade and leading to increased volatility in financial markets.
During pandemics, investors may become more risk-averse and seek safe-haven assets such as gold, which can cause an increase in demand and, in turn, drive up the price of gold CFDs. The COVID-19 pandemic is an example of this. When the pandemic hit in early 2020, global financial markets experienced significant volatility, and investors rushed to safe-haven assets such as gold, causing its price to surge to all-time highs.
On the other hand, pandemics can also have negative effects on the demand for gold. For example, during the Ebola outbreak in West Africa in 2014, the demand for gold jewelry, which is a significant source of demand for gold, declined sharply. This was because the outbreak led to a decline in economic activity and consumer confidence, which affected consumers' purchasing power.

Pandemics can also impact the supply of gold. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, gold mines in some countries were forced to shut down temporarily due to lockdowns and restrictions on movement, leading to a decline in the supply of gold.
Accidents
Accidents are another external factor that can affect the price of gold CFDs. Accidents can have different impacts on the price of gold CFDs depending on the type and severity of the accident. For example, accidents in mining or production facilities can disrupt the supply chain and affect the availability of gold, leading to a potential increase in its price. In contrast, accidents that affect the demand for gold, such as those that affect the jewelry industry, can lead to a decrease in the price of gold.
Accidents such as oil spills, nuclear disasters, and industrial accidents can also impact the price of gold. These events can cause environmental damage, disrupt trade, and lead to economic uncertainty. For instance, the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in 2010 led to a decline in the value of the US dollar and a rise in the price of gold.
Another example of an accident that affected the price of gold CFDs is the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico in 2010. The spill had a significant impact on the environment and the economy, which led to a decrease in demand for oil and, consequently, a decrease in demand for gold. However, the long-term environmental and economic impacts of the disaster could increase demand for gold in the future, particularly as investors may view it as a safe-haven asset in uncertain times.
Other Unforeseeable Events
External factors that can affect the price of gold CFDs are unforeseeable events such as natural calamities, pandemics, and accidents. These events can cause sudden fluctuations in the gold market and affect its price significantly. Here are a few examples:
● Cyber Attacks: Cyber attacks can disrupt financial markets and cause panic among investors, which may lead to a flight to safety in gold.
● Natural Resource Discoveries: The discovery of a significant new source of gold or other precious metals can affect the price of gold CFDs by increasing supply and reducing demand for other assets.
● Technological Advances: Technological advances in the mining and extraction of gold can increase supply and put downward pressure on prices.
III. Explanation and Analysis of the Factors
A. Geopolitical Factors
1. Political Instability
Impact of political instability in gold-producing nations
Political instability in gold-producing nations can have a significant impact on the price of gold CFDs. These nations may experience civil unrest, social upheaval, and conflicts that can disrupt mining operations and supply chains, leading to a decrease in the supply of gold. For example, in 2019, political unrest in Mali, which is Africa's third-largest gold producer, led to the closure of several mines, causing a decrease in gold production and affecting the global supply chain of gold. This led to an increase in the price of gold.

Additionally, political instability in gold-producing nations can also lead to changes in government policies and regulations that may impact the production and export of gold. For instance, in 2017, Tanzania banned the export of gold and copper concentrates, leading to a decrease in gold supply and a subsequent increase in the price of gold.
Moreover, political instability in gold-producing nations can affect investor confidence and result in a flight to safe-haven assets such as gold. For example, during the political crisis in Zimbabwe in 2017, the price of gold rose significantly due to investors seeking refuge in the metal.
Impact of political instability in major economies
Political instability in major economies can have a significant impact on the price of gold CFDs. This is because major economies such as the United States, China, and the European Union have a significant influence on the global financial system. Any major political instability in these economies can cause uncertainty and instability in the financial markets, leading investors to seek out safe-haven assets like gold.
For example, the 2008 financial crisis in the United States led to a significant increase in the price of gold as investors lost confidence in the financial system and turned to gold as a safe-haven asset. Similarly, the ongoing trade tensions between the United States and China have caused fluctuations in the price of gold as investors weigh the potential impact of the tensions on the global economy.
In addition, political instability in major economies can also lead to changes in government policies, such as changes in interest rates or fiscal policies, which can also affect the price of gold. For instance, the US Federal Reserve's decision to lower interest rates in response to the COVID-19 pandemic has contributed to the recent rise in gold prices.
Furthermore, political instability in major gold-producing nations can also have a significant impact on the price of gold. For example, political instability in South Africa, which is a major gold-producing country, can disrupt mining operations and lead to supply chain disruptions, thereby affecting the supply and demand dynamics of gold and ultimately influencing the price of gold CFD.
2. Global Tensions
Trade tensions
Trade tensions between major economies can also have a significant impact on the price of gold CFDs. When trade relations between countries deteriorate, it can lead to a decrease in global economic activity and a rise in uncertainty, causing investors to seek out safe-haven assets such as gold.
For example, the ongoing trade tensions between the US and China in recent years have had a significant impact on the price of gold CFDs. As the two countries imposed tariffs on each other's goods, global economic growth slowed, and investors turned to gold as a safe haven. In 2019, gold prices hit their highest level in six years as tensions between the US and China escalated.
Similarly, the trade tensions between the US and Europe in 2018 also contributed to an increase in the price of gold CFDs. As the US threatened to impose tariffs on European imports, investors sought out safe-haven assets such as gold, causing prices to rise.
Military tensions
Military tensions refer to the tensions or conflicts between countries or regions that involve the use or threat of military force. These tensions can have a significant impact on the price of gold CFDs as investors seek safe-haven assets during times of uncertainty.
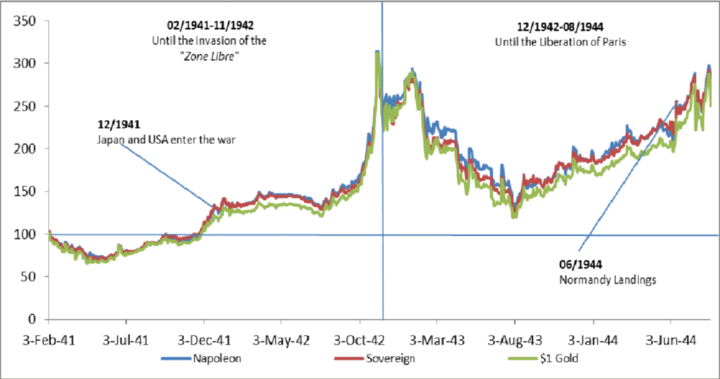
One example of military tensions impacting the price of gold CFDs is the ongoing conflict between the United States and Iran. In early January 2020, the U.S. carried out a drone strike that killed Iranian General Qasem Soleimani, which led to increased tensions between the two countries. In response, Iran fired missiles at U.S. military bases in Iraq, further escalating the conflict. As a result, the price of gold rose to a seven-year high as investors sought to protect their assets from potential economic and political fallout.
Another example is the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine. The annexation of Crimea by Russia in 2014 led to heightened tensions between the two countries, and the conflict has continued to escalate over the years. In 2021, reports of a Russian military buildup near the border with Ukraine led to increased uncertainty and a rise in the price of gold as investors sought safe-haven assets.
Impact on gold prices
Global tensions refer to the overall state of unease and instability in the international arena, such as conflicts between countries, terrorism, and civil unrest. Global tensions can have a significant impact on the price of gold CFDs due to their perceived safe-haven status. Investors tend to turn to gold as a hedge against uncertainty and risk in times of global turmoil.
For example, in 2019, the escalating tensions between the US and Iran following the assassination of Iranian General Qasem Soleimani led to a rise in gold prices. The uncertainty surrounding the potential for military conflict in the region and the possibility of disruptions in oil supplies caused investors to turn to gold as a safe-haven asset.
Similarly, the ongoing tensions between the US and China over trade and technology have also contributed to an increase in gold prices. The trade war has led to concerns about a global economic slowdown, causing investors to seek out safe-haven assets like gold.
In addition, political tensions within a country can also affect the price of gold. For instance, in 2021, the military coup in Myanmar led to a surge in gold prices as investors sought safe-haven assets amid the country's political instability and uncertainty.
3. Government policies and economic sanctions
Central Bank actions
Central bank actions can have a significant impact on the price of gold CFDs. Central banks hold large reserves of gold, and their buying and selling decisions can influence the market. When central banks buy gold, it signals a belief that the economy is weakening, and investors tend to flock to safe-haven assets like gold, driving up the price. On the other hand, when central banks sell gold, it can lead to a decrease in the price of gold as investors interpret it as a sign of economic stability.
For example, in 2019, central banks were net buyers of gold, with Russia and China leading the way. Russia increased its gold reserves by 158 tons in the first half of 2019, while China increased its gold reserves for the seventh straight month in June. These actions helped push the price of gold to a six-year high in September 2019.
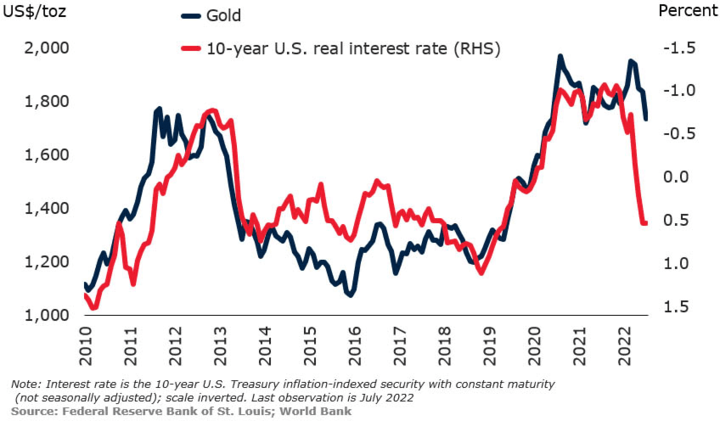
Another example is the action of the US Federal Reserve. When the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates, it can lead to inflation concerns, which can drive investors to safe-haven assets like gold. In 2020, the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates to near zero in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to a surge in gold prices as investors sought safe-haven assets amidst economic uncertainty.
Value of the national currency and exchange rate
Government policies and economic sanctions can also have a significant impact on the price of gold CFDs through their effects on the value of national currencies and exchange rates.
When a country's government implements policies that weaken its currency, the price of gold usually rises because gold is seen as a safe-haven asset that retains its value better than fiat currencies. For example, if a government decides to print more money to stimulate the economy or pay off its debts, this can lead to inflation and a decrease in the value of the currency. As a result, investors may turn to gold as a hedge against inflation and a store of value, driving up the price of gold CFDs.
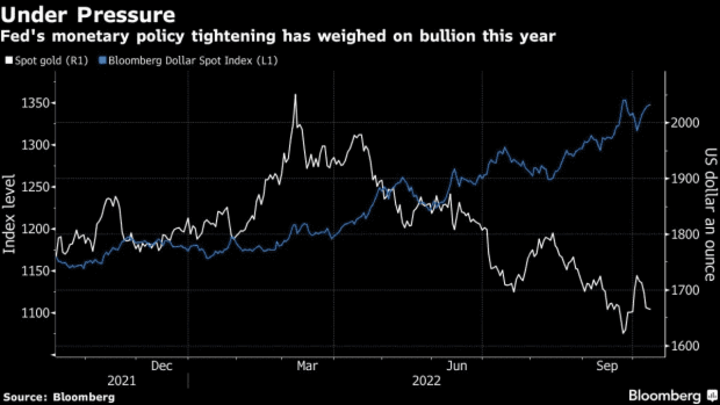
On the other hand, if a country's government implements policies that strengthen its currency, the price of gold may fall because it becomes relatively more expensive for investors holding other currencies to buy gold. For example, if a central bank raises interest rates to combat inflation, this can attract foreign investment and increase demand for the country's currency, causing it to appreciate against other currencies. As a result, the price of gold may decline as investors shift their funds to take advantage of higher yields in the strengthening currency.
Similarly, economic sanctions can also have a significant impact on a country's exchange rate and thus the price of gold. When a country is subjected to economic sanctions, its ability to trade with other countries is restricted, leading to a decrease in demand for its currency. As a result, the value of the currency may decline, leading to an increase in the price of gold CFDs as investors seek to hedge against the uncertainty and volatility caused by the sanctions.
For example, in 2018, the US imposed sanctions on Iran, restricting its access to the global financial system and hindering its ability to export oil. This led to a sharp depreciation in the value of the Iranian rial and a surge in demand for gold as a hedge against the resulting economic turmoil. Similarly, in 2014, the EU and US imposed sanctions on Russia, leading to a decline in the value of the Russian ruble and an increase in the price of gold as investors sought to protect their wealth from the uncertainty caused by the sanctions.
Economic sanctions and gold prices
Economic sanctions are one of the significant geopolitical factors that can affect the price of gold CFDs. When a country imposes economic sanctions on another country, it restricts or prohibits trade and financial transactions between the two nations. The targeted country may face difficulties in importing goods and exporting its resources, leading to a decrease in its economy's overall performance. As a result, the value of its currency can decrease, making gold relatively more attractive as a safe-haven asset.
For instance, in 2019, the United States imposed economic sanctions on Iran, which significantly affected the Iranian economy. As a result, the Iranian rial (IRR) lost value against other currencies, making gold an attractive option for Iranians to hedge against the devaluation of their currency. As a result, gold prices rose in Iran, with demand for physical gold increasing.
Similarly, in 2014, the United States and the European Union imposed economic sanctions on Russia for its annexation of Crimea. These sanctions led to a significant decrease in the value of the Russian ruble, making gold a more attractive option for investors to hedge against the devaluation of their currency. As a result, gold prices in Russia rose, and demand for physical gold increased.
4. Wars and Conflicts
Historical correlation between wars and gold prices
There has been a historical correlation between wars and gold prices. Gold has long been considered a safe-haven asset in times of political and economic turmoil, and wars often create uncertainty and instability, leading investors to seek safe-haven assets like gold. The price of gold tends to rise during times of war or geopolitical tensions as investors seek to hedge against the uncertainty and potential economic disruption caused by armed conflicts.
For example, during World War II, the price of gold skyrocketed as the world was engulfed in conflict. Similarly, during the Vietnam War and the Gulf War, the price of gold rose significantly as investors sought to protect their assets from the uncertain geopolitical environment. More recently, tensions between the US and North Korea in 2017 and 2018 led to a rise in gold prices.
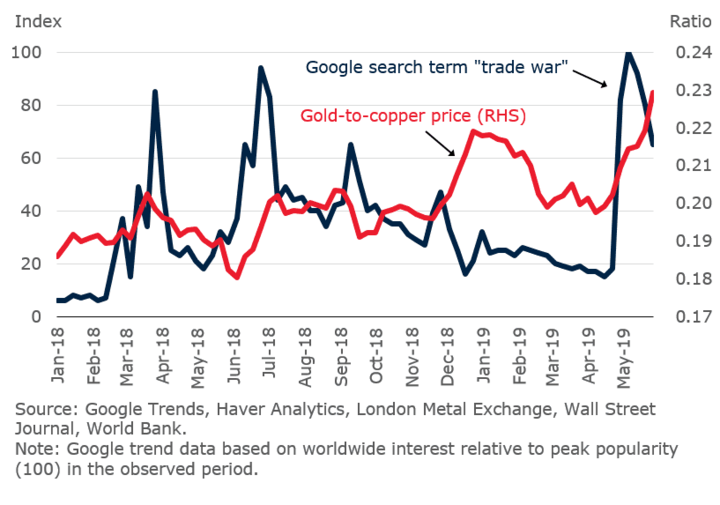
However, it's worth noting that the impact of wars and conflicts on gold prices can be unpredictable and can vary depending on a variety of factors, such as the duration of the conflict, the scale of the conflict, and the perceived threat to global stability. Additionally, other factors, such as central bank policies and economic data, can also affect gold prices during times of war or geopolitical tensions.
Impact of current wars and conflicts on gold prices
Current wars and conflicts can have a significant impact on the price of gold CFDs. When there is political unrest and military tension in the world, investors tend to move towards safe-haven assets like gold, which can increase its demand and price. The uncertainty and fear associated with wars and conflicts can also drive investors to seek out safe-haven assets.
For example, the ongoing conflict in Eastern Europe (Russia and Ukraine) and the tensions between the United States and China in recent years have led to increased demand for gold, driving its prices higher. In 2019, after a U.S. drone strike killed a top Iranian military commander, gold prices rose sharply due to concerns about a potential escalation of conflict between the two nations.
However, it's worth noting that the impact of wars and conflicts on gold prices can be unpredictable and short-lived. For instance, gold prices quickly dropped after the United States and North Korea held a summit in 2018, despite tensions between the two nations remaining high. Additionally, if the conflict is resolved quickly or there is a peaceful resolution, the impact on gold prices may be limited.
B. Economic Factors
1. Interest Rates
Relationship between interest rates and gold prices
The relationship between interest rates and gold prices is complex and can be influenced by a variety of factors. Generally speaking, when interest rates are low, gold prices tend to rise, and when interest rates are high, gold prices tend to fall. This is because when interest rates are low, there is less incentive for investors to hold onto cash or bonds, which offer low returns. Instead, they may turn to other assets, such as gold, which can offer a more attractive return.
Conversely, when interest rates are high, investors may prefer to hold onto cash or bonds as they offer a higher return and may be less inclined to invest in gold. Additionally, higher interest rates can lead to a stronger national currency, which can also put downward pressure on gold prices.
However, this relationship is not always clear-cut. There are other factors that can influence gold prices, such as inflation expectations, geopolitical tensions, and market sentiment. For example, if inflation is expected to rise, investors may turn to gold as a hedge against inflation, regardless of interest rates.
Furthermore, the impact of interest rates on gold prices can vary depending on the type of interest rates being considered. For example, the Federal Reserve's target interest rate, known as the federal funds rate, may have a more direct impact on gold prices than longer-term bond yields, such as the 10-year Treasury yield.
Impact of monetary policies
Monetary policy decisions made by central banks can have a significant impact on interest rates and, in turn, affect the price of gold. When central banks raise interest rates, it becomes more expensive to borrow money, which can reduce spending and slow down inflation. Higher interest rates can also strengthen the value of the currency, making it more expensive for foreign buyers to purchase gold, which can reduce demand for gold.
On the other hand, when central banks lower interest rates, it becomes cheaper to borrow money, which can stimulate spending and inflation. Lower interest rates can also weaken the value of the currency, making it less expensive for foreign buyers to purchase gold, which can increase demand for gold.
For example, in response to the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, many central banks around the world, including the Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank, lowered interest rates to stimulate economic growth. This led to an increase in the price of gold as investors sought out safe-haven assets amid the uncertainty and volatility caused by the pandemic.
2. Inflation
Relationship between inflation and gold prices
Inflation is one of the most important economic factors that affects the price of gold. The relationship between inflation and gold prices is positive. This means that as inflation rises, the price of gold tends to rise as well, and when inflation falls, the price of gold tends to fall too.
This is because gold is often seen as a hedge against inflation. When the purchasing power of paper currency decreases due to inflation, investors and traders turn to gold as a safe-haven asset, which can hold its value better in times of inflation. Since gold is priced in US dollars, inflation in the US can lead to a weaker dollar, which in turn can drive up the price of gold.
For example, during the 1970s, the US experienced high levels of inflation due to the oil crisis and other factors. During this time, the price of gold rose sharply, from around $35 per ounce in 1970 to over $800 per ounce by 1980. In more recent times, gold prices have also risen in response to inflation concerns, such as during the COVID-19 pandemic, when central banks around the world implemented quantitative easing measures to stimulate the economy.
However, it is important to note that inflation is not the only factor that affects the price of gold, and other economic and geopolitical factors can also have an impact. Additionally, the relationship between inflation and gold prices is not always linear and can be influenced by a variety of complex factors.
Impact of inflation on the value of currency and gold prices
Inflation can have a significant impact on the value of currency and, in turn, the price of gold. When inflation is high, the purchasing power of currency decreases, meaning that it can buy fewer goods and services. In response, investors may turn to gold as a safe-haven asset that retains its value even during times of inflation.
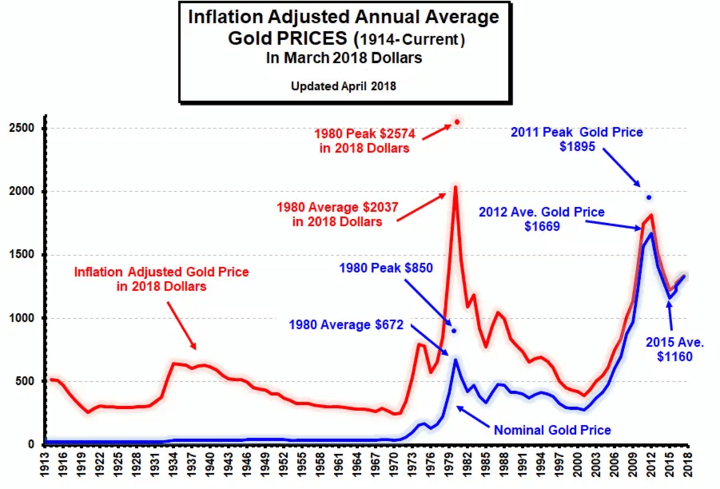
For example, during the 1970s, the United States experienced high levels of inflation due to factors such as rising oil prices and the Vietnam War. As a result, the value of the US dollar decreased, and the price of gold increased from around $35 per ounce in 1971 to over $800 per ounce by 1980.
Similarly, in more recent times, concerns about inflation have led to increased demand for gold. In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic caused significant economic disruption, and central banks around the world responded by implementing measures to stimulate the economy, such as lowering interest rates and increasing the money supply. This has led to fears of inflation, and as a result, the price of gold increased from around $1,500 per ounce in March 2020 to over $2,000 per ounce by August 2020.
3. Currency Exchange Rates
Relationship between currency exchange rates and gold prices
The relationship between currency exchange rates and gold prices is an important factor that affects the price of gold CFDs. Gold is priced in US dollars, and therefore, any changes in currency exchange rates can have a significant impact on the price of gold.
When the US dollar weakens, the price of gold typically rises, and when the US dollar strengthens, the price of gold typically falls. This is because when the US dollar weakens, investors may buy gold as a hedge against inflation and a way to protect their wealth. On the other hand, when the US dollar strengthens, investors may sell their gold holdings, as the stronger US dollar makes gold relatively more expensive for foreign buyers.
Moreover, currency exchange rates are also influenced by other economic factors, such as interest rates, inflation, and geopolitical events, all of which can indirectly affect the price of gold.
For example, if a country experiences high inflation, its central bank may raise interest rates to curb inflation, which can strengthen the country's currency. A stronger currency can make gold relatively more expensive for foreign buyers, leading to a decrease in demand and, consequently, a fall in the price of gold.
Similarly, if there is a geopolitical event that causes uncertainty and volatility in the currency markets, such as a political crisis or a war, investors may flock to safe-haven assets such as gold, leading to an increase in demand and a rise in the price of gold.
Impact of currency fluctuations on gold prices
Currency exchange rates play a significant role in determining the price of gold CFDs. When the value of a country's currency depreciates relative to other currencies, the price of gold denominated in that currency will generally rise. This is because gold becomes relatively cheaper for buyers who hold stronger currencies, and so demand for gold increases, causing its price to rise.
For example, let's consider the relationship between the US dollar and gold prices. Historically, the US dollar has been the world's reserve currency, and many international transactions are conducted in dollars. As a result, when the value of the US dollar weakens, the price of gold often rises. This is because investors and central banks may shift their focus towards gold as a store of value in response to concerns about the strength of the US dollar.
Another example is the relationship between the Chinese yuan and gold prices. China is the world's largest consumer of gold, and so any significant changes in the value of the yuan can impact the demand for gold. For example, if the yuan weakens relative to other currencies, Chinese investors may seek to purchase more gold as a way of protecting their wealth. This increase in demand can lead to higher gold prices.
4. Supply and Demand
Relationship between supply and demand and gold prices
The supply and demand of gold have a significant impact on its price in the market. The basic economic principle of supply and demand applies to gold as well. The price of gold is determined by the amount of gold available in the market (supply) and the amount of gold that people want to buy (demand).
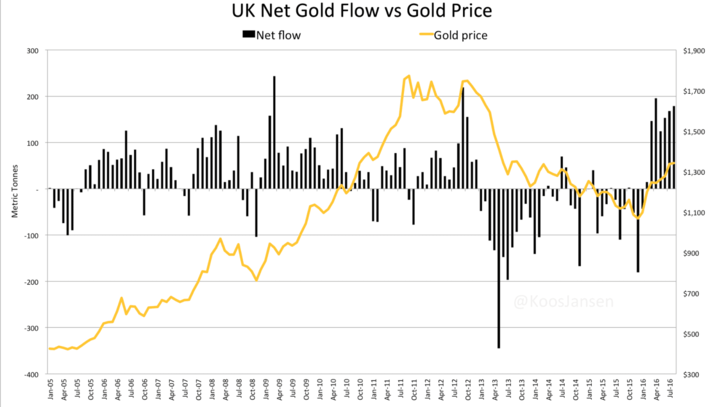
When the demand for gold is higher than its supply, the price of gold goes up. Conversely, when the supply of gold is higher than the demand, the price of gold goes down. The supply of gold mainly depends on the amount of gold produced from gold mines, while the demand for gold is influenced by various factors like jewelry, technology, investment, and central bank reserves.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for gold rose as investors looked for a safe haven to protect their investments. At the same time, the supply of gold was affected as gold mines had to shut down due to pandemic-related restrictions. As a result, the price of gold increased to an all-time high in 2020.
Another example is the impact of the jewelry industry on the supply and demand of gold. India is the world's largest consumer of gold for jewelry-making. During the wedding season in India, the demand for gold increases, leading to an increase in the price of gold. In contrast, if the demand for gold in the jewelry industry decreases, the price of gold may also decrease.
Impact of production and consumption trends on gold prices
The supply and demand of gold are major determinants of its price in the market. If the demand for gold is high and the supply is limited, the price of gold is likely to rise, and vice versa.
Gold production trends play a significant role in determining the supply of gold. A decrease in gold production can cause a decrease in the supply of gold, which can lead to an increase in the price of gold. For example, when COVID-19 lockdowns were imposed in 2020, gold mining operations were disrupted, which led to a decline in gold production, a reduction in the supply of gold, and an increase in its price.
On the other hand, consumption trends play a significant role in determining the demand for gold. Gold is widely used in the jewelry industry and in the manufacturing of electronics, among other things. If the demand for gold from these industries is high, it can lead to an increase in the price of gold. For example, during festive seasons, the demand for gold jewelry in countries such as India and China increases, leading to an increase in the price of gold.
Other factors that can affect the supply and demand of gold include changes in government policies, mining regulations, and geopolitical tensions. For example, changes in regulations that make it easier or more difficult for mining companies to operate can have an impact on the supply of gold. Similarly, geopolitical tensions can cause a shift in demand for gold as investors turn to it as a safe-haven asset.
C. Market Factors
1. Speculation
Role of speculation in gold prices
Speculation plays a significant role in determining the price of gold. Speculation refers to the act of buying or selling gold with the expectation of profiting from future price changes rather than the intrinsic value of the metal itself. Speculators include hedge funds, institutional investors, and individual traders who buy or sell gold contracts based on their beliefs about future market conditions.
Speculators often rely on technical analysis and market indicators to make decisions about buying or selling gold. For example, a trader may analyze historical price data and look for patterns that suggest a change in market direction. Alternatively, a trader may rely on news events, such as geopolitical tensions or economic data releases, to predict future market movements and adjust their positions accordingly.
The impact of speculation on gold prices can be significant. For example, if speculators believe that the price of gold will increase in the future, they may buy large quantities of gold contracts, which can drive up the price of the metal. Conversely, if speculators believe that the price of gold will decrease, they may sell their contracts, which can cause the price of gold to fall.
Speculation can also create volatility in the gold market. Because speculators make decisions based on their perceptions of future market conditions, their actions can cause sudden and unexpected price movements, which can make it difficult for investors to accurately predict the direction of the market.
Impact of speculation on future gold prices
Speculation is a major driver of gold prices, as many investors buy and sell gold based on their expectations of future price movements. Speculators may base their predictions on a variety of factors, including economic data, political events, and global trends. As a result, the impact of speculation on gold prices can be difficult to predict and can lead to significant volatility in the market.
For example, if investors expect that economic growth will slow down, they may buy gold as a safe-haven asset, driving up the price. Conversely, if investors expect interest rates to rise, they may sell gold and buy other investments that offer higher returns, causing the price of gold to fall.
One notable example of the impact of speculation on gold prices was during the financial crisis of 2008. As investors became increasingly concerned about the stability of financial markets, they began buying up gold as a safe-haven asset. This led to a significant increase in the price of gold, which rose from around $800 per ounce in early 2008 to a high of over $1,900 per ounce in 2011.
However, speculation can also lead to rapid price declines in the gold market. In 2013, for example, rumors circulated that the Federal Reserve was planning to reduce its bond-buying program, which led to widespread selling of gold by investors. As a result, the price of gold fell by more than 25% in just a few months.
2. Investor Sentiment
Relationship between investor sentiment and gold prices
Investor sentiment refers to the overall attitude of investors towards the financial market and their perception of the risks and opportunities it presents. When investor sentiment is positive, investors are generally more willing to take on risk and invest in assets like stocks and currencies, which can lead to an increase in demand for those assets and drive up their prices. On the other hand, when investor sentiment is negative, investors may be more risk-averse and look to invest in safer assets like gold, which can lead to an increase in demand for gold and drive up its price.
The relationship between investor sentiment and gold prices is complex and can be influenced by a variety of factors, including economic conditions, geopolitical risks, and central bank policies. For example, during periods of economic uncertainty or geopolitical tensions, investors may become more risk-averse and seek safe-haven assets like gold, which can lead to an increase in demand for gold and drive up its price. Conversely, during periods of economic growth and stability, investors may be more willing to take on risk and invest in assets like stocks, which can lead to a decrease in demand for gold and drive down its price.
One example of investor sentiment affecting the price of gold was during the global financial crisis of 2008. As the crisis unfolded and investor sentiment turned negative, demand for safe-haven assets like gold surged, driving up its price to record levels. Similarly, during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, investor sentiment again turned negative, leading to a surge in demand for gold and driving up its price to over $2,000 per ounce.
Impact of positive or negative sentiment on gold prices
Investor sentiment plays a significant role in determining the price of gold. Positive investor sentiment towards gold leads to an increase in demand for the commodity, leading to an increase in its price. Conversely, negative investor sentiment can lead to a decrease in demand and, subsequently, a decrease in the price of gold.
One example of how investor sentiment affects gold prices is during times of economic uncertainty. When investors are uncertain about the future of the economy, they may seek out safe-haven assets like gold to protect their investments. This increase in demand can lead to an increase in the price of gold. On the other hand, when investors are optimistic about the economy, they may be less likely to invest in safe-haven assets, leading to a decrease in demand and a subsequent decrease in the price of gold.
Another example is how investor sentiment can be influenced by geopolitical events. For instance, political instability or tensions between countries can lead to increased investor anxiety, resulting in a higher demand for safe-haven assets like gold. In such cases, the price of gold tends to rise. Conversely, when geopolitical tensions ease or a resolution is reached, investors may become more confident and opt for other investments, leading to a decline in demand and a corresponding decrease in gold prices.
3. Stock Market Movement
Relationship between stock market movement and gold prices
The relationship between stock market movements and gold prices is complex and multifaceted. Generally, there is an inverse correlation between the two, meaning that when the stock market goes up, gold prices tend to go down, and vice versa. This is because investors often view gold as a safe-haven asset that can protect their portfolio in times of economic uncertainty, while stocks are considered riskier investments that tend to perform well during periods of economic growth.
However, there are several factors that can complicate this relationship. For example, during times of inflation, both gold and stocks may perform well as investors look for assets that can protect them against rising prices. Additionally, there may be periods when both gold and stocks are seen as attractive investments, leading to a positive correlation between the two.
One example of the relationship between stock market movements and gold prices occurred during the 2008 financial crisis. As the stock market plummeted, investors flocked to gold as a safe-haven asset, driving up its price. Similarly, during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, as stock markets experienced extreme volatility, gold prices surged to record highs as investors sought a hedge against economic uncertainty.
On the other hand, during periods of economic growth when the stock market is performing well, gold prices tend to fall. For example, during the bull market of the 2010s, as the stock market reached record highs, gold prices were relatively low. This is because investors were more willing to take on risk and invest in stocks rather than hold onto safe-haven assets like gold.
Impact of stock market volatility on gold prices
The relationship between stock market movements and gold prices can be complex and multifaceted, with a variety of factors influencing both markets. In general, there is often an inverse correlation between the two, meaning that when stock prices rise, gold prices tend to fall, and vice versa. This is because investors often view stocks as a higher-risk, higher-reward investment, while gold is seen as a safe-haven asset in times of uncertainty.
However, it's important to note that this relationship is not always consistent or predictable. For example, there may be times when both stock and gold prices are rising because investors are bullish on both markets. Additionally, other external factors such as inflation, geopolitical tensions, and central bank policies can also influence both markets independently of each other.
One key way that stock market volatility can impact gold prices is by driving investors to seek out safe-haven assets like gold during times of uncertainty or economic turbulence. This can lead to increased demand for gold, driving up prices. Conversely, if the stock market is performing well and investors feel confident in the economy, there may be less demand for gold as a safe-haven asset, leading to lower prices.
For example, during the financial crisis of 2008, when stock markets around the world were experiencing significant volatility and uncertainty, gold prices surged to all-time highs as investors flocked to the safety of the precious metal. Similarly, during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, as global stock markets experienced sharp declines, gold prices again rose to near all-time highs as investors sought out safe-haven assets.
4. Commodity Market Movement
Relationship between commodity market movement and gold prices
The commodity market is a broad category that includes various raw materials and resources. While gold is considered a precious metal, it is also a commodity that is traded on the market. Therefore, the movement of the commodity market can impact the price of gold CFDs.
There are several ways in which commodity market movements can impact the price of gold CFDs. First, the supply and demand of other commodities can indirectly affect the demand for gold. For example, if the supply of oil decreases, it can lead to an increase in its price, which can then lead to higher inflation rates. This can drive investors towards gold as a hedge against inflation, increasing its demand and price.
Second, the overall sentiment in the commodity market can also influence the price of gold. For example, if the market experiences a bullish trend, investors may have a positive outlook on the economy and therefore choose to invest in riskier assets such as stocks, resulting in a decrease in demand for gold. Conversely, if the market experiences a bearish trend, investors may have a negative outlook on the economy and therefore choose to invest in safe-haven assets such as gold, resulting in an increase in demand for gold and its price.
Third, the movement of other commodities such as silver, copper, or platinum can also impact the price of gold CFDs, as these metals are often traded alongside gold as part of a precious metals portfolio.
Impact of commodity market volatility on gold prices
Commodity market movements can have a significant impact on the price of gold CFDs, as gold is considered a commodity and is often traded alongside other commodities. When there is increased volatility in commodity markets, it can lead to changes in supply and demand dynamics for gold, which can in turn impact its price.
For example, if there is a sudden increase in demand for oil due to geopolitical tensions, it could lead to higher oil prices, which can then impact the price of gold. This is because higher oil prices could lead to higher production costs for gold mining companies, which could lead to lower gold supply and higher gold prices.
Similarly, a decrease in demand for industrial metals such as copper could also impact the price of gold. This is because copper is often used in manufacturing and construction, and a decrease in demand for copper could indicate a slowdown in the global economy. This could lead investors to seek safe-haven assets such as gold, leading to an increase in demand and higher prices.
D. External Factors
1. Natural Disasters
Impact of natural disasters on gold prices
Natural disasters can have a significant impact on the price of gold, as investors often turn to gold as a safe-haven asset during times of uncertainty and instability. When a natural disaster occurs, such as a hurricane, earthquake, or flood, it can disrupt economic activity and cause uncertainty about the future, leading investors to seek out safe haven assets like gold.
One example of this was the impact of Hurricane Katrina on gold prices in 2005. The hurricane caused widespread damage and destruction in the southern United States, leading to a sharp rise in the price of gold as investors sought refuge from the uncertainty and instability caused by the disaster.
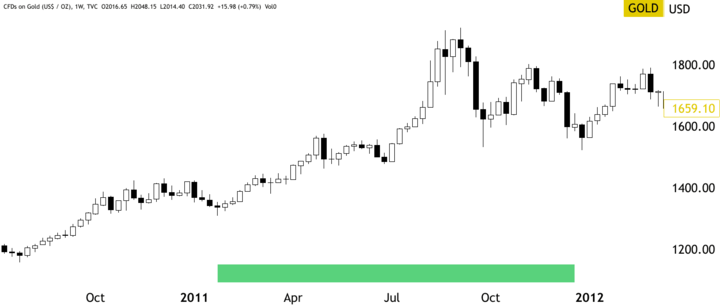
Similarly, the earthquake and tsunami that hit Japan in 2011 also had a significant impact on gold prices. In the aftermath of the disaster, investors turned to gold as a safe-haven asset, causing the price of gold to rise sharply.
In addition to natural disasters, other unexpected events, such as pandemics and terrorist attacks, can also have an impact on gold prices. For example, the outbreak of COVID-19 in early 2020 caused a significant rise in the price of gold as investors sought refuge from the economic uncertainty caused by the pandemic.
Examples of natural disasters and their impact on gold prices
Natural disasters can have a significant impact on gold prices due to their effect on the global economy and investor sentiment. Here are some examples:
Hurricane Katrina: In August 2005, Hurricane Katrina hit the United States and caused significant damage to the oil and gas infrastructure in the Gulf of Mexico. The disruption in the supply of energy resulted in a surge in energy prices, which led to a rise in inflation and a decline in the value of the US dollar. This, in turn, caused an increase in the price of gold, which is often seen as a hedge against inflation and a safe-haven asset in times of economic uncertainty.
Australian bushfires: In early 2020, bushfires ravaged large parts of Australia, causing widespread damage to property and infrastructure. The fires also had a significant impact on the country's economy, with industries such as tourism and agriculture suffering losses. The economic uncertainty caused by the fires resulted in a surge in demand for safe-haven assets such as gold, which led to an increase in its price.
2. Pandemics
Impact of pandemics on gold prices
Pandemics can have a significant impact on global economies and financial markets, including the price of gold. The outbreak of a pandemic can cause panic among investors, leading them to seek safe-haven assets like gold. This increased demand can drive up the price of gold.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, which began in early 2020, the price of gold reached record highs. As the virus spread globally, investors became increasingly concerned about the economic impact and sought the safety of gold. This led to a surge in demand for gold, driving up the price.
Similarly, during the 2003 SARS epidemic, which primarily affected Asia, the price of gold increased by 4%. Investors were concerned about the potential economic impact of the disease and sought the safety of gold.
However, the impact of pandemics on gold prices can also depend on the severity and duration of the outbreak. If a pandemic is contained quickly and does not have a significant impact on the global economy, its effect on gold prices may be minimal.
Examples of pandemics and their impact on gold prices
The outbreak of pandemics can have a significant impact on the global economy and financial markets, including the price of gold CFDs.
One recent example is the COVID-19 pandemic, which started in early 2020 and spread rapidly around the world, leading to global lockdowns and economic disruptions. As the pandemic caused uncertainty and fear among investors, many of them turned to gold as a safe-haven asset, leading to a surge in demand and an increase in the price of gold.
During the first quarter of 2020, when the pandemic began to spread globally, the price of gold increased by around 6% as investors sought a safe haven amid the market turmoil caused by the pandemic. The price of gold continued to increase throughout 2020, hitting an all-time high of $2,067 per ounce in August 2020.
Another example is the 2003 SARS pandemic, which originated in China and quickly spread to other parts of the world. As with the COVID-19 pandemic, the outbreak of SARS caused widespread fear and uncertainty among investors, leading to an increase in the demand for gold as a safe-haven asset. The price of gold increased by around 3% during the outbreak of SARS in 2003.
3. Accidents
Impact of accidents on gold prices
Accidents, especially those related to mining, can have an impact on the price of gold. This is because gold mining is a major source of the supply of gold, and any disruptions in the supply chain can affect the price. Accidents can lead to mine closures, production delays, or a reduction in the quality of gold produced, all of which can affect the supply of gold in the market.
Accidents can also have a psychological impact on the market, as they can create fear and uncertainty among investors. This can cause them to seek out safe-haven assets such as gold, which can drive up prices. Therefore, accidents should not be overlooked as a potential factor affecting the price of gold CFDs.
Examples of accidents and their impact on gold prices
For example, in 2015, a dam at a Brazilian mining site owned by Vale SA and BHP Billiton ruptured, causing a significant amount of toxic waste to spill into the surrounding area. This accident caused the temporary closure of the mine and disrupted the supply of iron ore, which is often extracted alongside gold. The disruption in the supply of iron ore and the closure of the mine caused the price of gold to increase as investors sought a safe haven asset amidst the market uncertainty.
Similarly, in 2019, a major accident occurred at the Porgera gold mine in Papua New Guinea, which is operated by Barrick Gold Corporation and Zijin Mining Group. The accident led to the suspension of operations at the mine and a reduction in the production of gold, causing a spike in the price of gold.
Also, the 2015 Samarco mining disaster in Brazil The disaster involved a dam collapse at an iron ore mine, but it also affected gold production in the region. As a result, gold prices increased due to concerns about supply shortages.
Another example is the 2011 earthquake and tsunami in Japan, which had a ripple effect on the gold market. The disaster caused a global economic slowdown and led to a decrease in demand for gold. However, the uncertainty and volatility caused by the event also led to an increase in the price of gold as investors sought safe-haven assets.
4. Other unforeseeable events
Explanation of other unforeseeable events and their impact on gold prices
Other unforeseeable events refer to unexpected events that are not covered by the previously mentioned factors but may still affect the price of gold. These events may include natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, accidents, pandemics, and unexpected economic shocks.
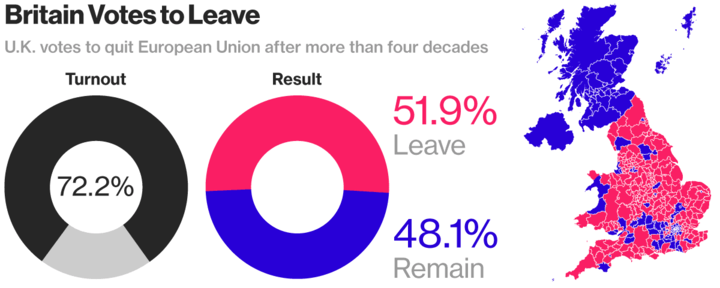
For example, the unexpected Brexit vote in 2016 caused uncertainty in the global financial markets, leading to a rise in gold prices as investors sought a safe-haven investment.
Other unforeseeable events that can affect the price of gold include unexpected natural disasters, such as earthquakes or hurricanes, which can disrupt supply chains and increase demand for safe-haven assets. Geopolitical tensions, such as wars or terrorist attacks, can also cause a flight to safety and drive up the price of gold.
Examples of unforeseeable events and their impact on gold prices
Other unforeseeable events refer to unexpected occurrences that can impact the global economy and financial markets, including the price of gold. These events can range from natural disasters to political turmoil to unexpected economic shocks.
One example of an unforeseeable event that had a significant impact on gold prices was the 2008 financial crisis. The crisis was caused by the collapse of the US housing market and resulted in a global economic downturn. As investors sought safe-haven assets to protect their portfolios, the price of gold rose significantly. In 2008, gold prices increased by more than 25% as investors rushed to buy the precious metal.
Other examples of unforeseeable events that can impact gold prices include geopolitical tensions, terrorist attacks, and natural disasters like hurricanes and earthquakes. For instance, the 9/11 terrorist attacks in 2001 caused gold prices to rise due to the uncertainty and fear they created in the global financial markets.
IV. Conclusion
Summary of the factors that affect the price of gold CFD
There are several factors that can impact the price of gold CFDs. One of the key drivers is the overall economic climate, which can influence investor sentiment and demand for safe-haven assets such as gold. Interest rates and inflation also play an important role, as changes in monetary policy can impact currency values and therefore the relative value of gold. Additionally, supply and demand dynamics in the gold market, as well as production and consumption trends, can also impact prices. The role of speculation cannot be ignored, as market sentiment and expectations of future events can drive prices in either direction. Finally, unforeseeable events such as natural disasters or pandemics can also have a significant impact on gold prices, as investors may seek out the relative safety of gold during times of uncertainty. Overall, understanding these various factors and how they interact with each other is important for predicting and analyzing movements in the gold CFD market.

Recommendations for traders to consider when trading gold CFDs
● Stay informed about the market: Keep up-to-date with the latest news and events that can impact the price of gold, such as economic reports, monetary policies, and geopolitical events.
● Use Technical Analysis: The analysis can help traders identify trends and potential trading opportunities. It involves studying chart patterns, price action, and other market indicators to make informed trading decisions.
● Manage risk: Trading gold CFDs involves a certain level of risk. To minimize potential losses, traders should use stop-loss orders and limit orders to set their exit points.
● Diversify your portfolio: Traders should consider diversifying their portfolio by including other assets, such as stocks, currencies, and commodities, to reduce their exposure to risk.
● Choose a reliable broker: When trading gold CFDs, it's important to choose a reliable broker with a good reputation and a solid track record. This will help ensure that your trades are executed quickly and accurately and that your funds are secure.


The importance of monitoring the latest news and events
Monitoring the latest news and events is crucial in today's fast-paced and interconnected world, especially for traders and investors. The global economy is highly volatile, and various factors such as political instability, natural disasters, pandemics, and market fluctuations can significantly impact the financial markets, including the price of commodities such as gold.
Keeping up-to-date with the latest news and events helps traders identify potential opportunities and risks, adjust their trading strategies, and make informed decisions. For instance, if a major political event or announcement affects the currency exchange rates, it can directly impact the price of gold, and traders who are aware of this can use it to their advantage.
In summary, staying informed about the latest news and events is crucial for traders who want to succeed in the financial markets, including trading gold CFDs. It helps them stay ahead of the curve and make better-informed and logical trading decisions, leading to favorable profitability.