Oil CFD trading has emerged as a popular investment avenue for traders seeking exposure to the oil market.
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) offer a flexible and efficient way to speculate on the price movements of crude oil without owning the physical commodity. With the recent developments in the oil industry and the dynamic nature of global markets in 2023, staying informed and adapting your trading strategies is crucial.
In the world of oil CFD trading, knowledge is power. Understanding the fundamentals of oil markets, supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical factors, and technical analysis is vital for making informed trading decisions. Keeping up with the latest news, trends, and market indicators is essential to identify potential trading opportunities and manage risks effectively.

Image Source: freepik
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the fundamentals of oil CFD trading, including essential strategies, risks involved, and best practices. Whether you are a beginner looking to dip your toes into trading or an experienced trader aiming to refine your skills, this article will provide you with the insights and confidence to successfully navigate the world of oil CFDs.
So, let's dive in and explore the exciting possibilities of oil CFD trading together.
Understanding Oil CFD
To trade oil CFDs with confidence, it's crucial to understand their definition and types. A Contract for Difference (CFD) is a derivative instrument that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of crude oil without owning the physical asset.
Two primary types of oil CFDs exist: West Texas Intermediate (WTI) and Brent Crude. WTI represents oil produced in the United States, while Brent Crude is sourced from the North Sea. Each type has its own price dynamics and market influences, requiring traders to stay updated on the latest developments in both markets.

Image Source: freepik
When trading oil CFDs, familiarize yourself with the contract specifications and margin requirements. CFD contracts have specific parameters such as lot size, tick value, and minimum trade size. Margin requirements vary between brokers and depend on factors like volatility and leverage. Understanding these details is important to manage your trading capital and risk exposure effectively.
Oil CFDs offer flexible trading hours and high liquidity, allowing traders to participate in the market conveniently. The trading hours typically mirror the underlying oil market, which is open for trading around the clock during weekdays. Liquidity ensures that there are sufficient buyers and sellers in the market, reducing the risk of slippage and enabling traders to enter and exit positions smoothly.
Understanding the intricacies of oil CFDs is essential to develop a successful trading strategy.
Setting up for Oil CFD Trading

Image Source: freepik
When embarking on your journey to trade oil CFDs, selecting a reputable CFD broker and setting up your trading account are critical steps. Consider the following factors:
Regulation and Licensing: Choose a broker regulated by a respected financial authority. Regulations provide a level of protection for your funds and ensure fair trading practices.
Trading Platform and Tools: Evaluate the trading platform offered by the broker. Ensure it is user-friendly, provides real-time market data, and offers advanced charting tools and indicators for technical analysis. A powerful trading platform can significantly enhance your trading experience.
Account Types and Funding: Review the account types available, such as standard accounts or accounts with specific features like Islamic accounts or VIP services. Additionally, consider the funding options available, including convenient deposit and withdrawal methods.
Moreover, while you trade oil CFDs, it's essential to select your trading instruments carefully. Consider the following factors:
WTI vs. Brent CFDs: Determine whether you want to trade West Texas Intermediate (WTI) or Brent Crude CFDs. Analyze their respective market dynamics, price correlations, and geopolitical influences to make an informed choice. Stay updated on the latest news and developments in both markets.
Analysis of Spread and Liquidity: Evaluate the spreads the broker offers for oil CFDs. Tighter spreads reduce trading costs. Additionally, assess the CFDs' liquidity, ensuring sufficient trading volume to execute your orders effectively.
Market Sentiment and Trend Analysis: Study market sentiment and conduct trend analysis to identify potential trading opportunities. Utilize technical indicators, chart patterns, and price action analysis to gauge the direction of oil prices. Stay abreast of fundamental factors like supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and economic indicators that impact oil prices.
Furthermore, understanding the differences between WTI and Brent CFDs, analyzing spreads and liquidity, and staying informed about market sentiment and trends will empower you to make confident trading decisions. With a reputable CFD broker, tools, and instrument selection, you can position yourself for success in the dynamic world of oil CFD trading.
In the next section, we will explore effective strategies, risk management techniques, and best practices to further enhance your oil CFD trading skills.
Trading Strategies

Image Source: freepik
To trade oil CFDs with confidence, employing effective trading strategies is essential. Trading strategies are predefined plans or approaches used by traders to make buying and selling decisions in financial markets.
They involve a set of rules or criteria based on technical, fundamental, or quantitative analysis to maximize profits and minimize risks. Here are three popular strategies to consider:
A. Technical analysis
Technical analysis is a trading strategy that involves studying historical price and volume data to forecast future price movements. It utilizes charts, indicators, and patterns to identify trends, support and resistance levels, and potential entry and exit points. Key components of technical analysis include:
Overview of Charts and Indicators: Familiarize yourself with different chart types, such as line charts, candlestick charts, and bar charts. Additionally, use technical indicators to gain insights into price trends and potential entry and exit points.
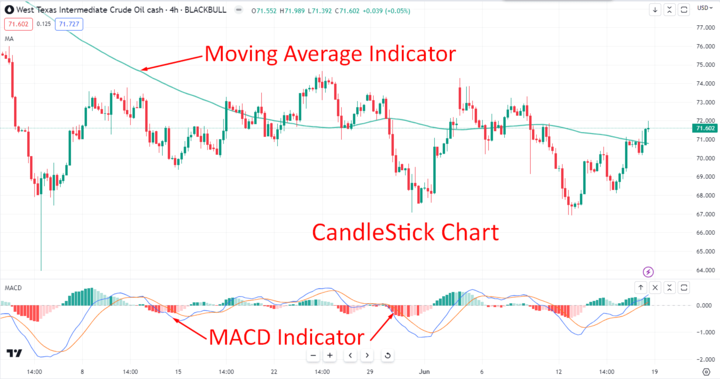
Image Source: Tradingview
Identifying Trends and Signals: Analyze price trends to determine whether the market is bullish (rising prices) or bearish (falling prices). Look for signals such as trendline breaks, moving average crossovers, or chart patterns like double tops and bottoms.
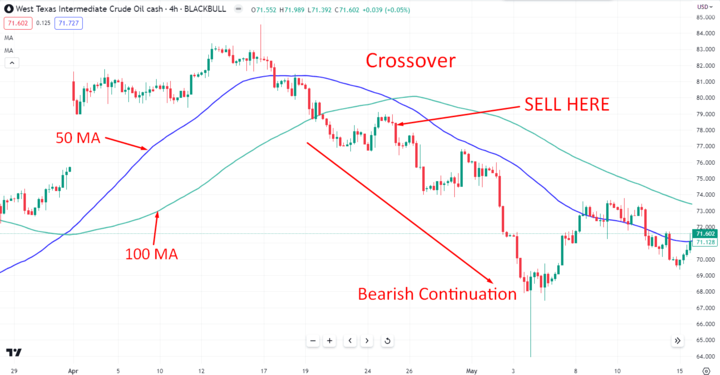
Image Source: Tradingview
Use of Moving Averages, RSI, MACD, and Bollinger Bands: Utilize popular technical indicators like moving averages to identify trend direction, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to gauge overbought or oversold conditions, the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to identify momentum shifts, and Bollinger Bands to identify potential breakouts or reversals.
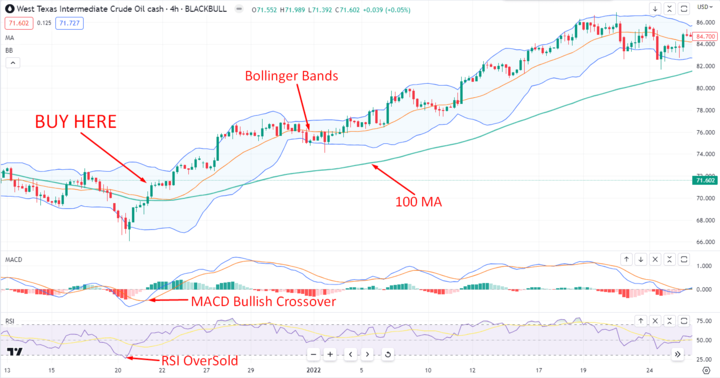
Image Source: Tradingview
Look for a buy trade when the price crosses above the 100 periods moving average line and close above the Bollinger Band’s middle band. Besides, the MACD line crosses above the signal line below the 0.00 level. Also, the RSI lines indicate an oversold situation in the market.
Conversely, Look for a sell trade when the price crosses below the 100 periods moving average line and close below the Bollinger Bands middle band. Besides, the MACD line crosses below the signal line above the 0.00 level. Also, the RSI lines indicate an overbought situation in the market.
B. Fundamental analysis
Fundamental analysis involves assessing economic and geopolitical factors that can influence oil prices. Consider the following aspects:
Analyzing Supply and Demand Data: Monitor supply and demand fundamentals, including inventory levels, production rates, and global demand forecasts. Understanding these factors helps you anticipate potential shifts in the oil market.
Geopolitical Events and Economic Indicators: Stay updated on geopolitical events, such as conflicts or sanctions, which can impact the oil supply. Additionally, pay attention to economic indicators like GDP growth, inflation rates, and interest rate decisions, as they can affect oil demand.
Identifying News and Events that Can Impact Prices: Follow news sources and industry reports to stay informed about major oil-related news, such as OPEC decisions, geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or changes in energy policies. These events can significantly impact oil prices.
C. Risk management
Image Source: freepik
Implementing effective risk management strategies is crucial to protect your capital and minimize potential losses. Risk management refers to the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks in trading and investment activities. It involves implementing strategies to protect capital and minimize potential losses while maximizing potential returns. Consider the following risk management techniques:
Setting Stop-Loss and Limit Orders: Determine your risk tolerance and set appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels for each trade. Stop-loss orders automatically close your position if prices move against you, while limit orders secure profits by closing positions when predetermined profit targets are reached.
Managing Trade Sizes and Leverage: Carefully consider your trade sizes in relation to your account balance to avoid overexposure. Also, leverage can amplify potential profits and increase losses, so use leverage judiciously and understand its associated risks.
Implementing Effective Risk Management Strategies: Utilize risk management techniques such as diversification (spreading your trades across different assets), trailing stops to protect profits, and regularly assessing and adjusting your risk-reward ratios.
Incorporating technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and effective risk management strategies into your oil CFD trading approach will enhance your decision-making process and improve your chances of trading confidently.
Executing and Monitoring Trades

Image Source: freepik
To trade oil CFDs with confidence, it's crucial to understand how to place and execute orders effectively. Executing trades refers to the process of placing orders and executing them in the market. It involves selecting the desired trade parameters, entering orders on the trading platform, and managing open positions effectively. Consider the following steps:
Types of Orders: Familiarize yourself with the different order types available. Market orders allow you to buy or sell at the current market price. Limit orders enable you to set a specific price at which you want to enter or exit a trade. Stop orders help limit potential losses by triggering a trade when the market moves against you. You can make informed decisions and execute trades efficiently by understanding these order types.
Placing Trades on Trading Platforms: Modern trading platforms provide user-friendly interfaces for placing trades. Take the time to explore and understand the features of your chosen platform. Enter the necessary trade details, including the order type, quantity, and desired entry and exit prices. Additionally, utilize advanced features such as stop-loss and take-profit orders to manage risk and potential profits.
Managing Open Positions: Once you have executed a trade, it's essential to actively manage your open positions. Regularly monitor price movements, assess profit and loss levels, and adjust your stop-loss and take-profit levels accordingly. Being disciplined and avoiding impulsive decisions based on short-term fluctuations can help you stay on track with your trading strategy.
Furthermore, successful oil CFD trading requires continuous monitoring of the market. Monitoring trades involves keeping a close eye on market movements and tracking the performance of open positions. Stay informed and adapt your strategies as needed using the following guidelines:


News and Data Releases: Stay updated on relevant news and economic data releases that can impact oil prices. Pay attention to reports related to oil inventories, production levels, geopolitical events, and economic indicators. News releases often cause significant price volatility, presenting both opportunities and risks. Stay informed about these events to make informed trading decisions.
Adapting Strategies According to Market Changes: Market conditions can change rapidly, requiring you to adapt your trading strategies. Analyze price movements, technical indicators, and news events to adjust your approach accordingly. For example, if you observe a significant increase in oil supply, you might consider adjusting your strategy to account for potential price declines. Flexibility is key to successful trading.
Taking Profits and Minimizing Losses: Regularly evaluate your trades and consider taking profits when your predetermined profit targets are reached. Similarly, if the market moves against you, use stop-loss orders to limit your losses. Strive for a favorable risk-to-reward ratio by aiming for larger profits compared to potential losses. Effective risk management is crucial for long-term success in trading.
By mastering order placement and execution and actively monitoring the market, you can enhance your trading skills and confidence when trading oil CFDs. These practices will help you to help protect your capital and optimize your trading outcomes.
Conclusion
Oil CFD trading offers several benefits, including the ability to profit from rising and falling oil prices, flexibility in trade sizes, and the convenience of online trading platforms.
This guide explored the fundamentals of trading oil CFDs and discussed strategies, risks, and best practices. We learned about technical and fundamental analysis techniques to identify trading opportunities and optimize profits.
Combining knowledge, discipline, and sound trading strategies allows you to embark on your journey from a beginner to a pro in the exciting world of oil CFD trading. Now that you have gained a solid foundation, it's time to put your knowledge into practice and embark on your trading journey. Wishing you success in your oil CFD trading endeavors!